How to outsmart your COVID-19 fears and boost your mood in 2021

Photo by panitan punpuang on Unsplash
After a year of toxic stress ignited by so much fear and uncertainty, now is a good time to reset, pay attention to your mental health and develop some healthy ways to manage the pressures going forward.
Brain science has led to some drug-free techniques that you can put to use right now.
I am health psychologist who developed a method that harnesses our rip-roaring emotions to rapidly switch off stress and activate positive emotions instead. This technique from emotional brain training is not perfect for everyone, but it can help many people break free of stress when they get stuck on negative thoughts.
Why the stress response is so hard to turn off
Three key things make it hard to turn off stress-activated negative emotions:
- First, our genes make us worrywarts. Our hunter-gatherer ancestors survived by assuming every rustle in the grasses was a lurking hungry lion, not harmless birds hunting for seeds. We’re essentially programmed to be hyperaware of threats, and our brains rapidly launch stress chemicals and negative emotions in response.
- Second, the chemical cascade of stress hormones in the brain associated with negative emotions impairs cognitive flexibility, goal-directed behavior and self-control.
- Third, our tendency to avoid dealing with negative emotions puts people in a perpetual cycle of ignoring unpleasant feelings, which amplifies stress and the risk of emotional health problems.
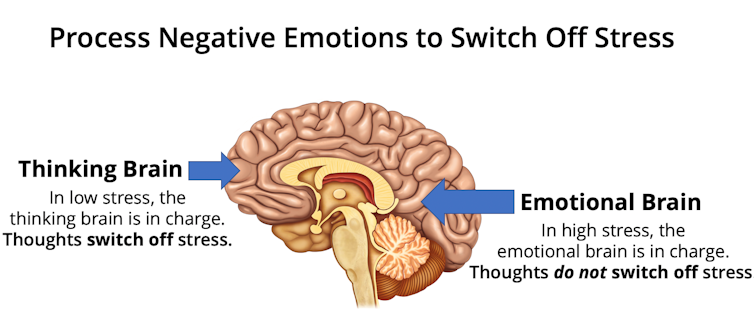
Thought vs. emotion in the brain.
Laurel Mellin, CC BY-ND
Traditional approaches for coping with stress were based on cognitive-behavioral therapy, which focuses on modifying patterns of thinking and behavior. It was developed before our modern understanding of stress overload.
Researchers at New York University discovered a paradox: Although cognitive methods were effective in low-stress situations, they were less effective when dealing with the high stress of modern life.
Emotional brain training works with these high-stress emotions in an effort to tame them, releasing negative emotions as the first of two steps in preventing stress overload.
Step 1: Release negative emotions
The only negative emotion in the brain that supports taking action rather than avoidance and passivity is anger.
Studies have shown that the suppression of anger is associated with depression and that suppressing anger doesn’t reduce the emotion. Healthy release of anger instead has been found to reduce other stress-related health risks.
Our technique is to switch off stress overload by using a controlled burst of anger to help the brain exert better emotional control and allow emotions to flow rather than become chronic and toxic. After that first short burst, other feelings can flow, starting with sadness to grieve the loss of safety, then fear and regret, or what we would do differently next time.
You can talk yourself through the stages. To experiment with the process, use these simple phrases to express the negative feelings and release your stress: “I feel angry that …”; “I feel sad that …”; “I feel afraid that …”; and “I feel guilty that …”
Step 2. Express positive emotions
After releasing negative emotions, positive emotions can naturally arise. Express these feelings using the same approach: “I feel grateful that …”; “I feel happy that …”; “I feel secure that …”; and “I feel proud that …”
Your mindset can quickly change, a phenomenon that has many potential explanations. One explanation is that in positive states, your brain’s neural circuits that store memories from when you were in the same positive state in the past can be spontaneously activated. Another is that the switch from negative to positive emotions quiets your sympathetic nervous system – which triggers the fight-or-flight response – and activates the parasympathetic system, which acts more like a brake on strong emotions.
Here’s what the whole stress relief process might look like like for me right now:
- I feel angry that we’re all isolated and I can’t see my new grandson Henry.
- I hate it that everything is so messed up! I HATE THAT!!!
- I feel sad that I am alone right now.
- I feel afraid that this will never end.
- I feel guilty that I am complaining! I am lucky to be alive and have shelter and love in my life.
Then the positive:
- I feel grateful that my daughter-in-law sends me photos of Henry.
- I feel happy that my husband and I laughed together this morning.
- I feel secure that this will eventually pass.
- I feel proud that I am doing the best I can to cope.
After a daunting year, and with more challenges ahead in 2021, upgrading your approach to emotions can be a drug-free mood booster. Our COVID-19 fears need not consume us. We can outsmart the brain’s fear response and find moments that sparkle with promise.
Laurel Mellin, Associate Professor Emeritus of Family & Community Medicine and Pediatrics, University of California, San Francisco
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.