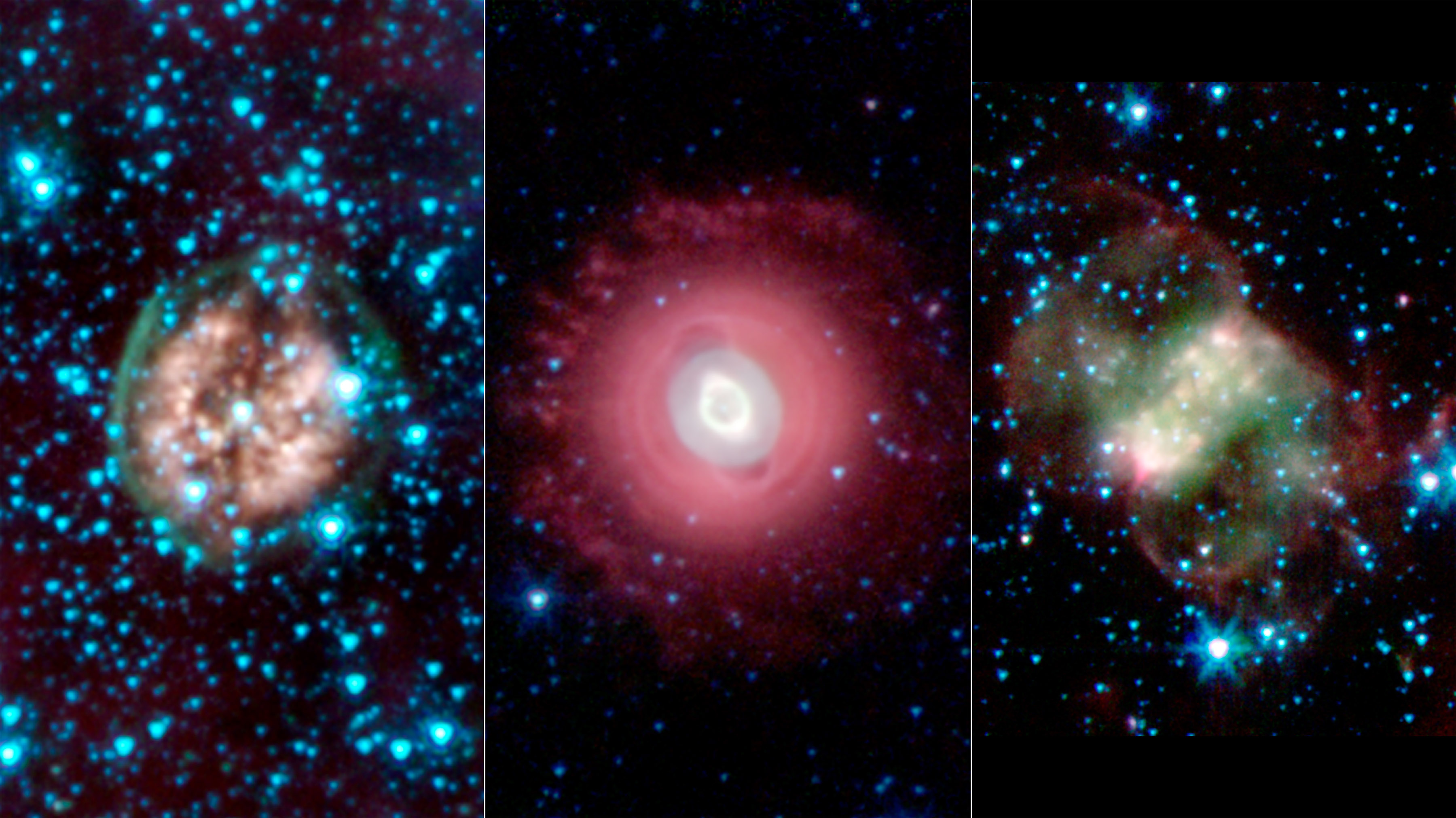
What kind of object will you form? What will its fate be? How long will a star live? Almost everything is determined by mass alone.
Search Results
You searched for: Saturn
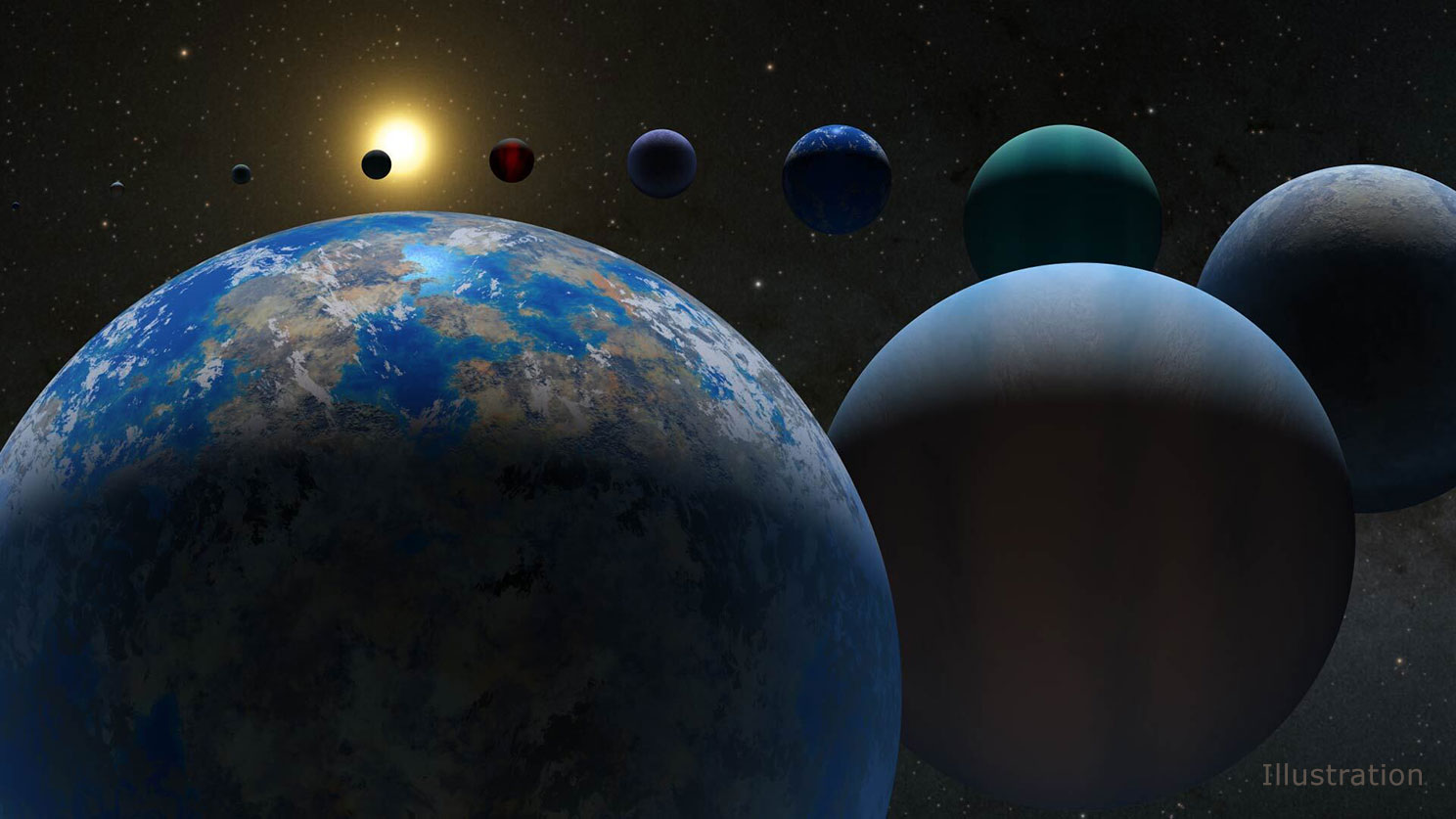
The number of planets that could support life may be far greater than previously thought, a recent discovery suggests.
Grab a sword, a small plate, and a young child. We’ve got a demon to summon.
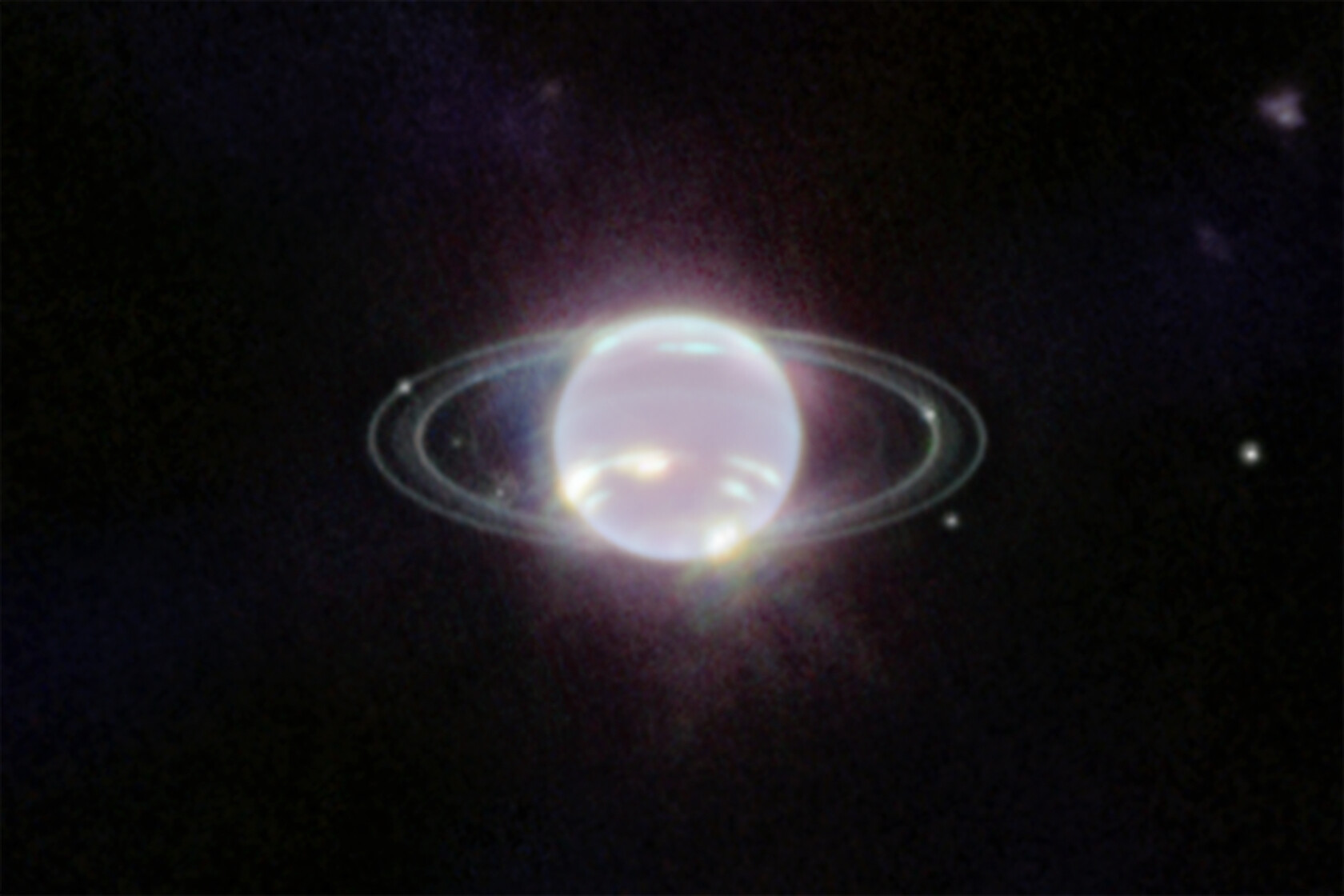
The James Webb Space Telescope viewed Neptune, our Solar System’s final planet, for the first time. Here’s what we saw, and what it means.
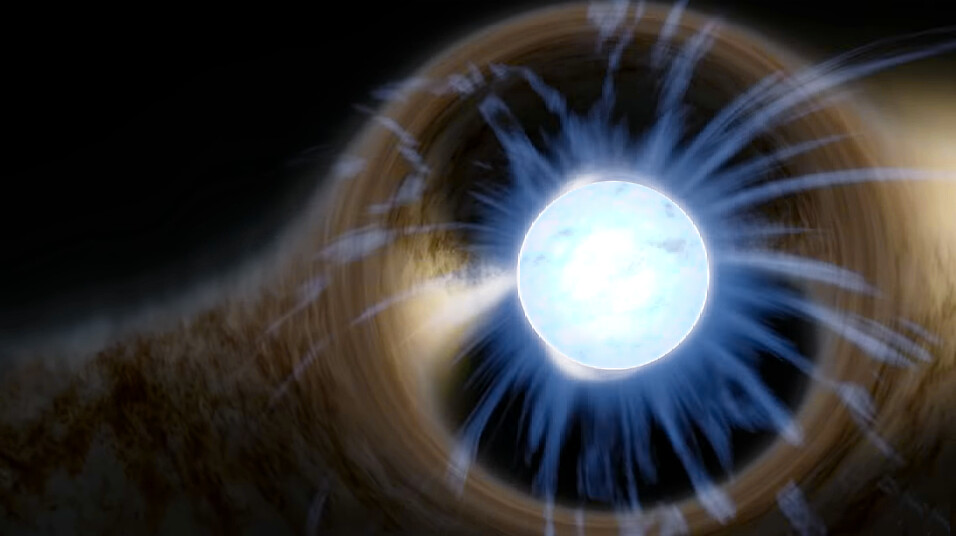
Neutrons can be stable when bound into an atomic nucleus, but free neutrons decay away in mere minutes. So how are neutron stars stable?
The structure of our Solar System has been known for centuries. When we finally started finding exoplanets, they surprised everyone.
Back in 1990, we hadn’t discovered a single planet outside of our Solar System. Here are 10 facts that would’ve surprised every astronomer.
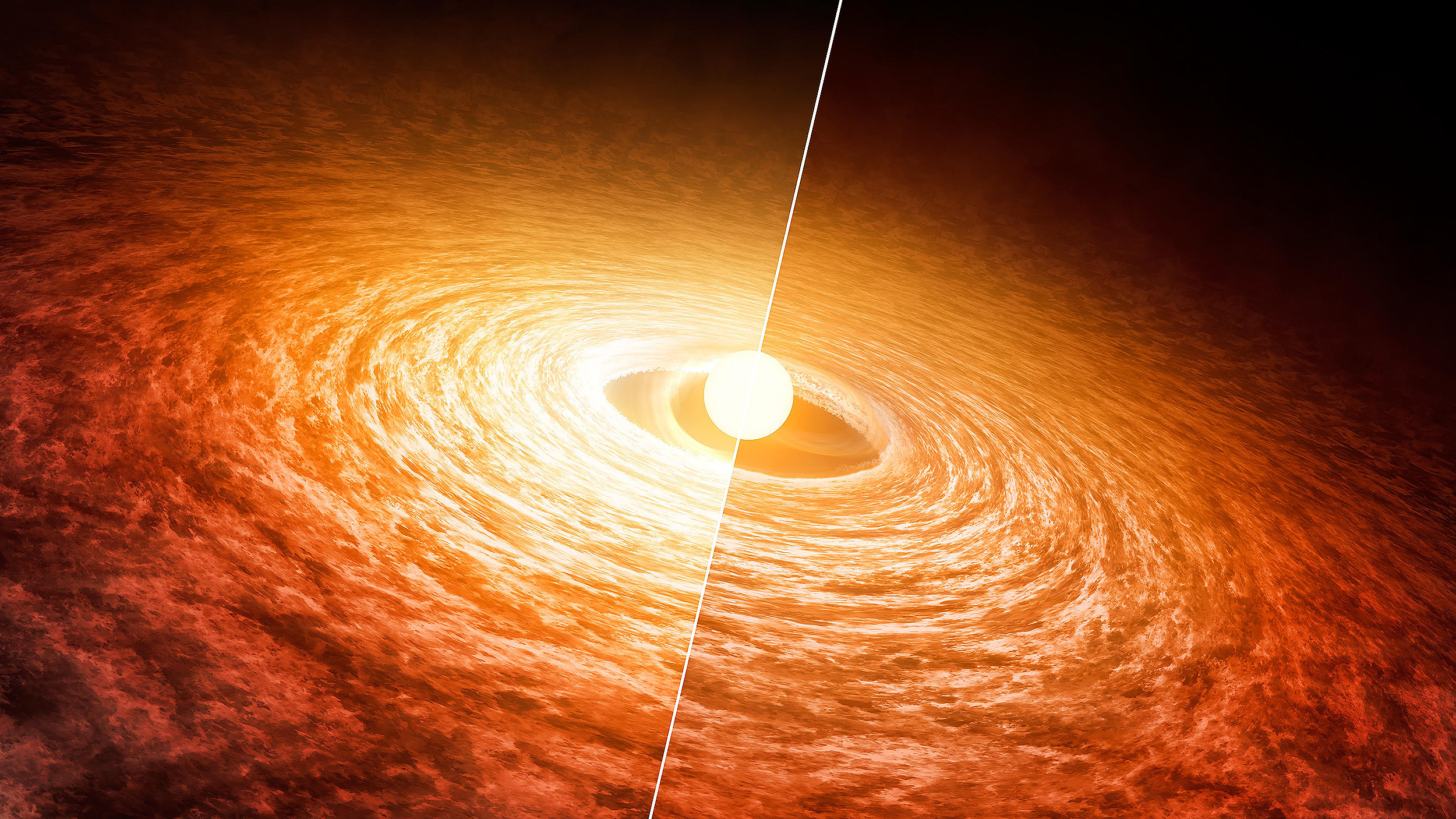
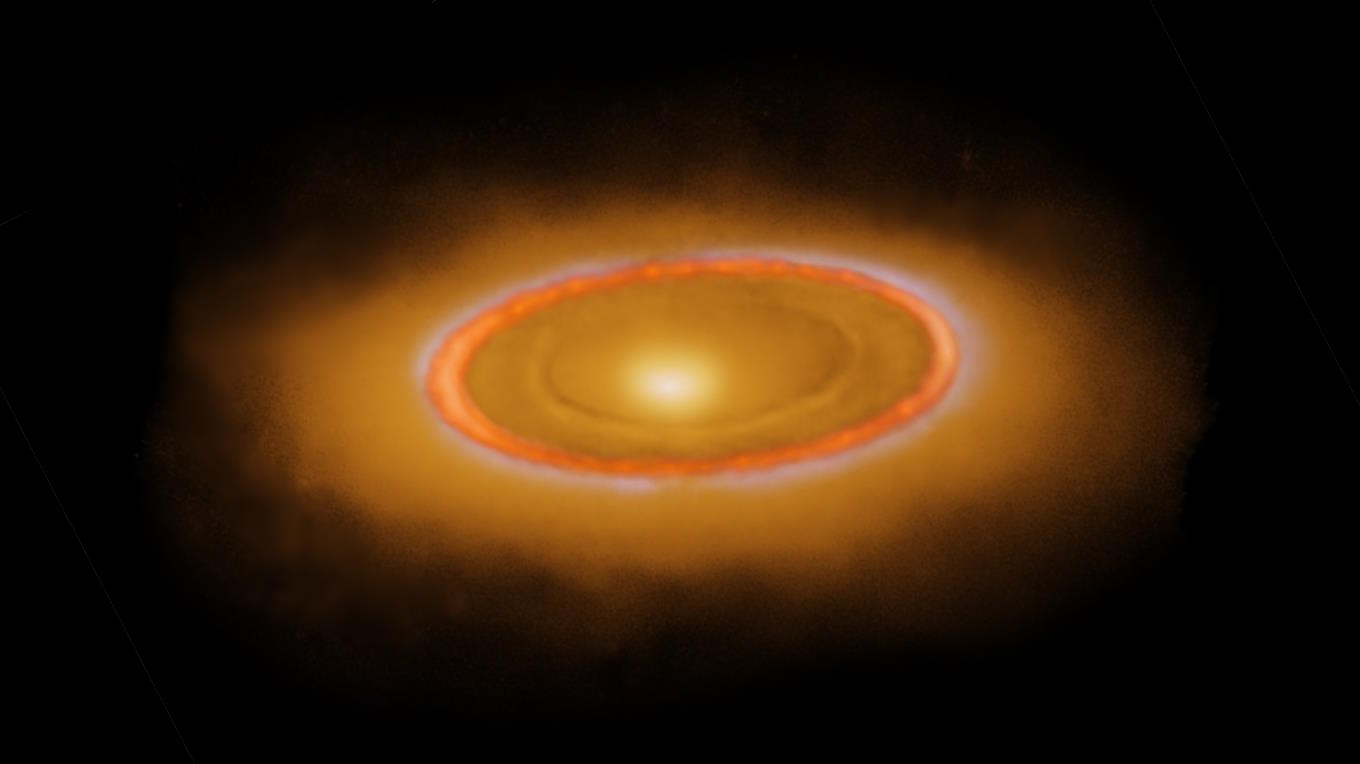
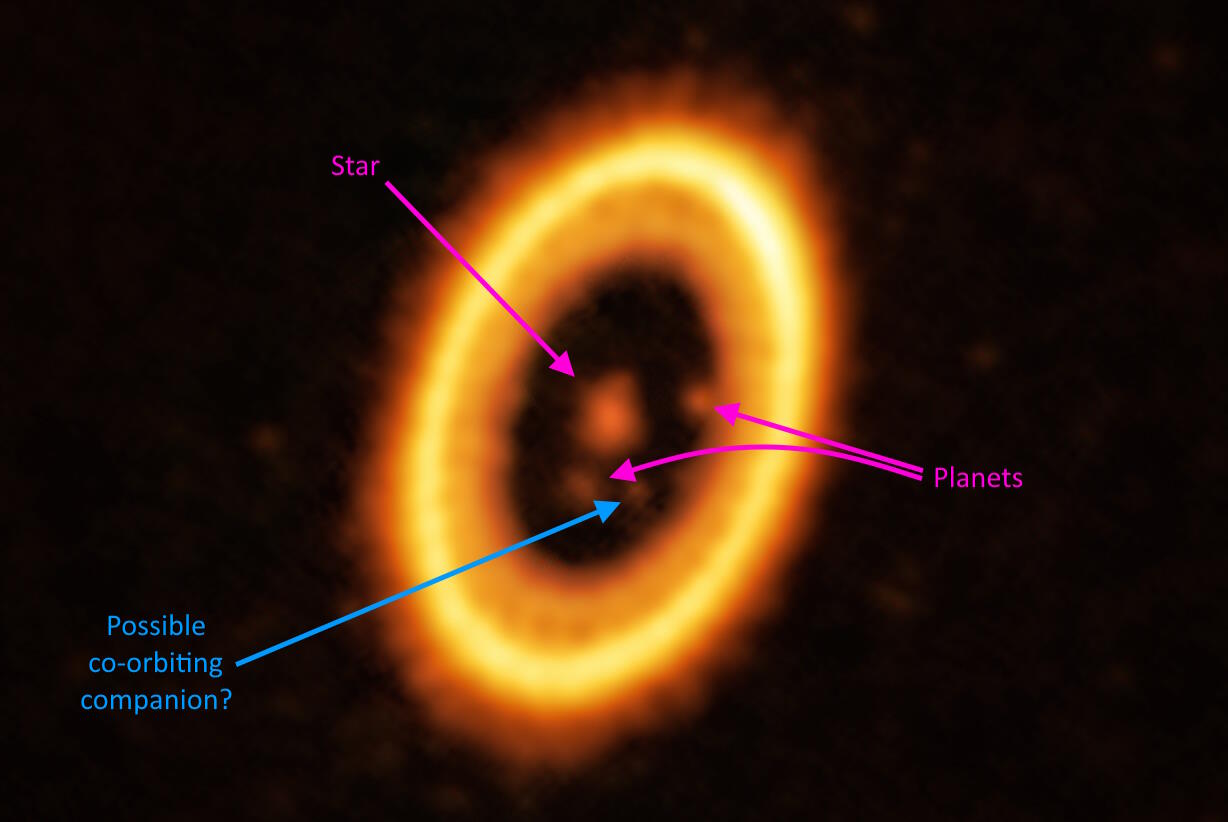
Newborn stars are surrounded only by a featureless disk. Debris disks persist for hundreds of millions of years. So when do planets form?
The giant impact theory suggests our Moon was formed from proto-Earth getting a Mars-sized strike. An exoplanet system shows it’s plausible.
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile will image the southern sky using the largest digital camera ever built.
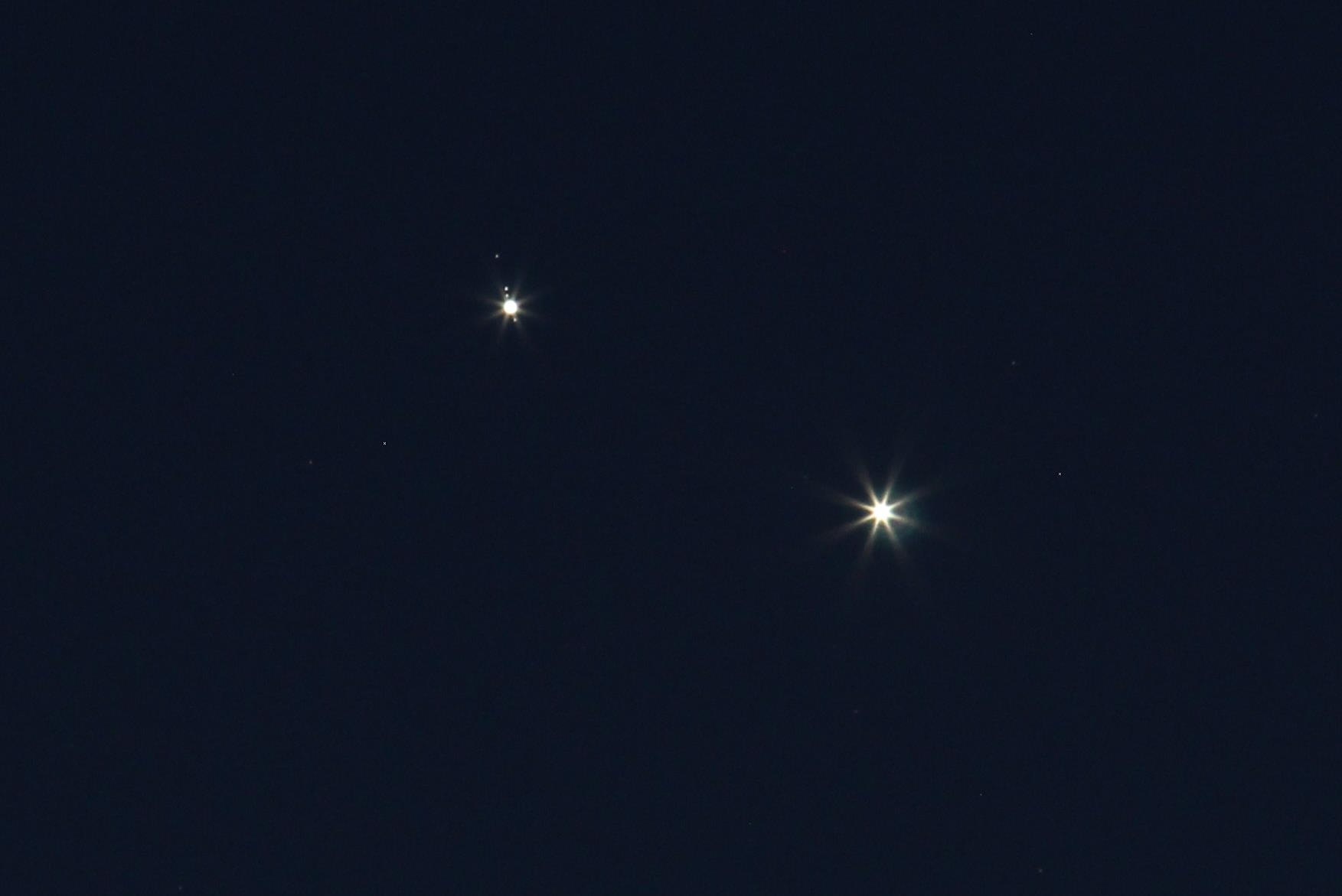
In our Solar System, even the two brightest planets frequently align in our skies. But only rarely is it spectacularly visible from Earth.
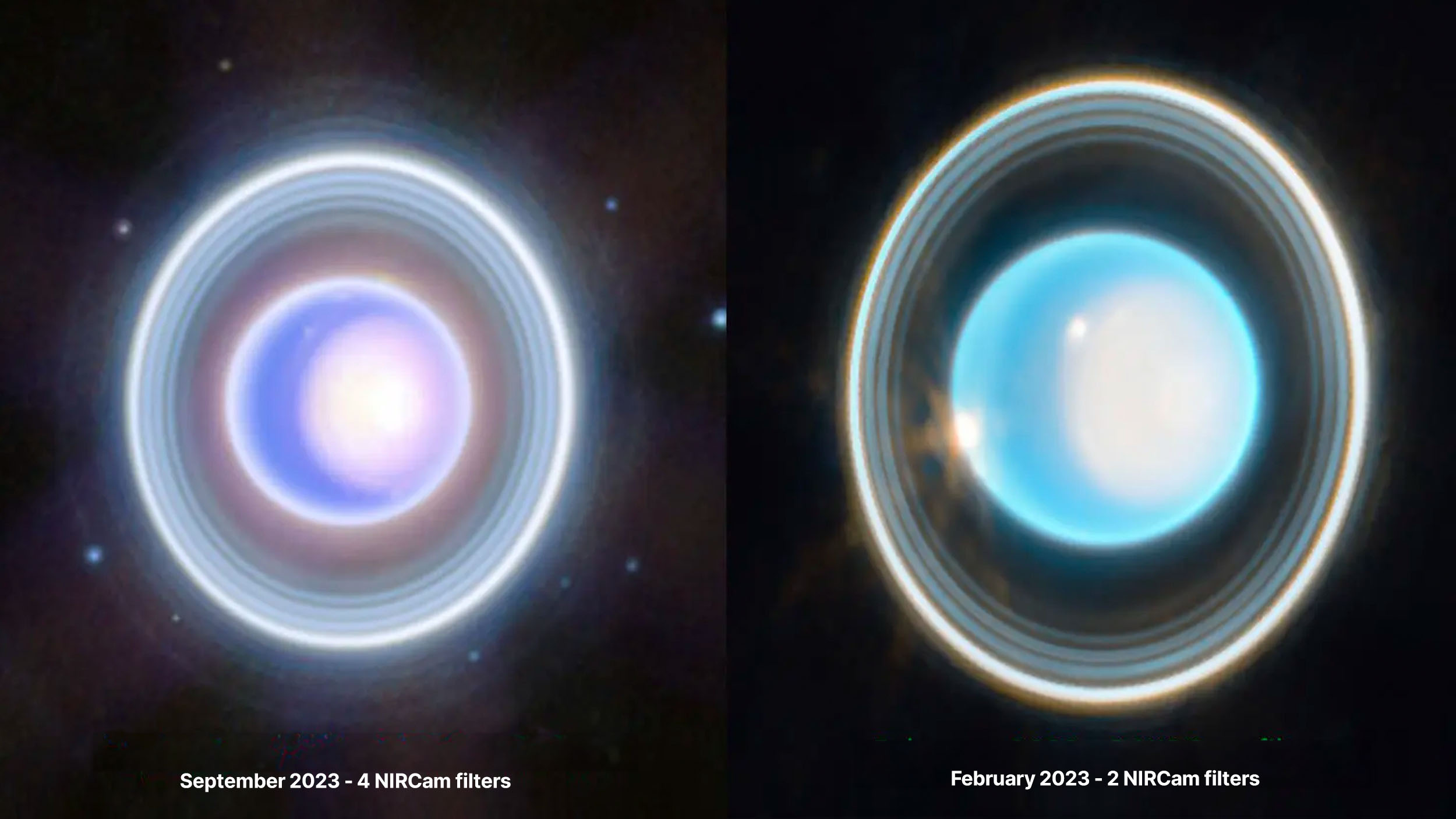
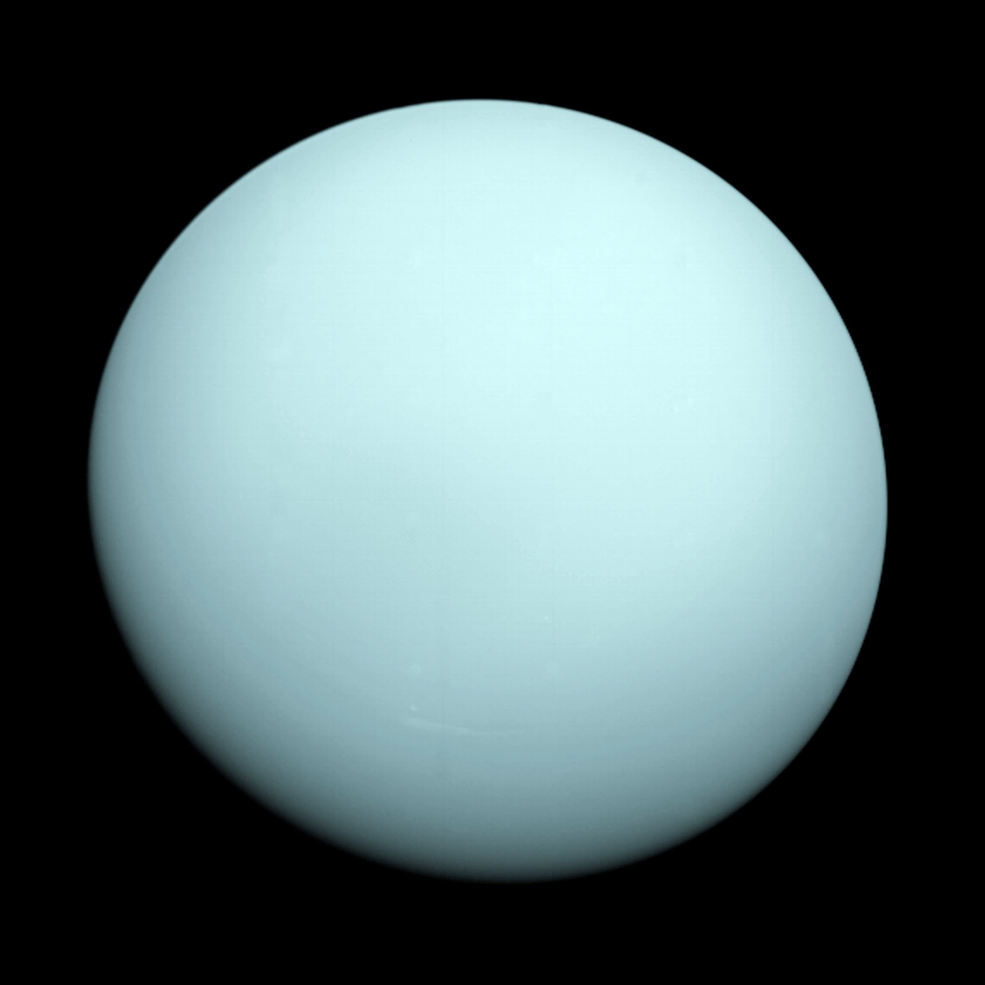
We’ve only seen Uranus up close once: from Voyager 2, back in 1986. The next time we do it, its features will look entirely different.
As Uranus approaches its solstice, its polar caps, rings, and moons come into their best focus ever under JWST’s watchful eye. See it now!
For some reason, when we talk about the age of stars, galaxies, and the Universe, we use “years” to measure time. Can we do better?
Some microbes can withstand Earth’s most inhospitable corners, hinting that life may be able to survive similarly extreme conditions on other worlds.
In the night sky for March of 2022, only stars and the Moon, not planets, will greet you. The real show, however, arrives just before dawn.
The space telescope’s findings challenge the notion of a galaxy brimming with life.
The nearby, bright star Fomalhaut had the first optically imaged planetary candidate. Using JWST’s eyes, astronomers found so much more.
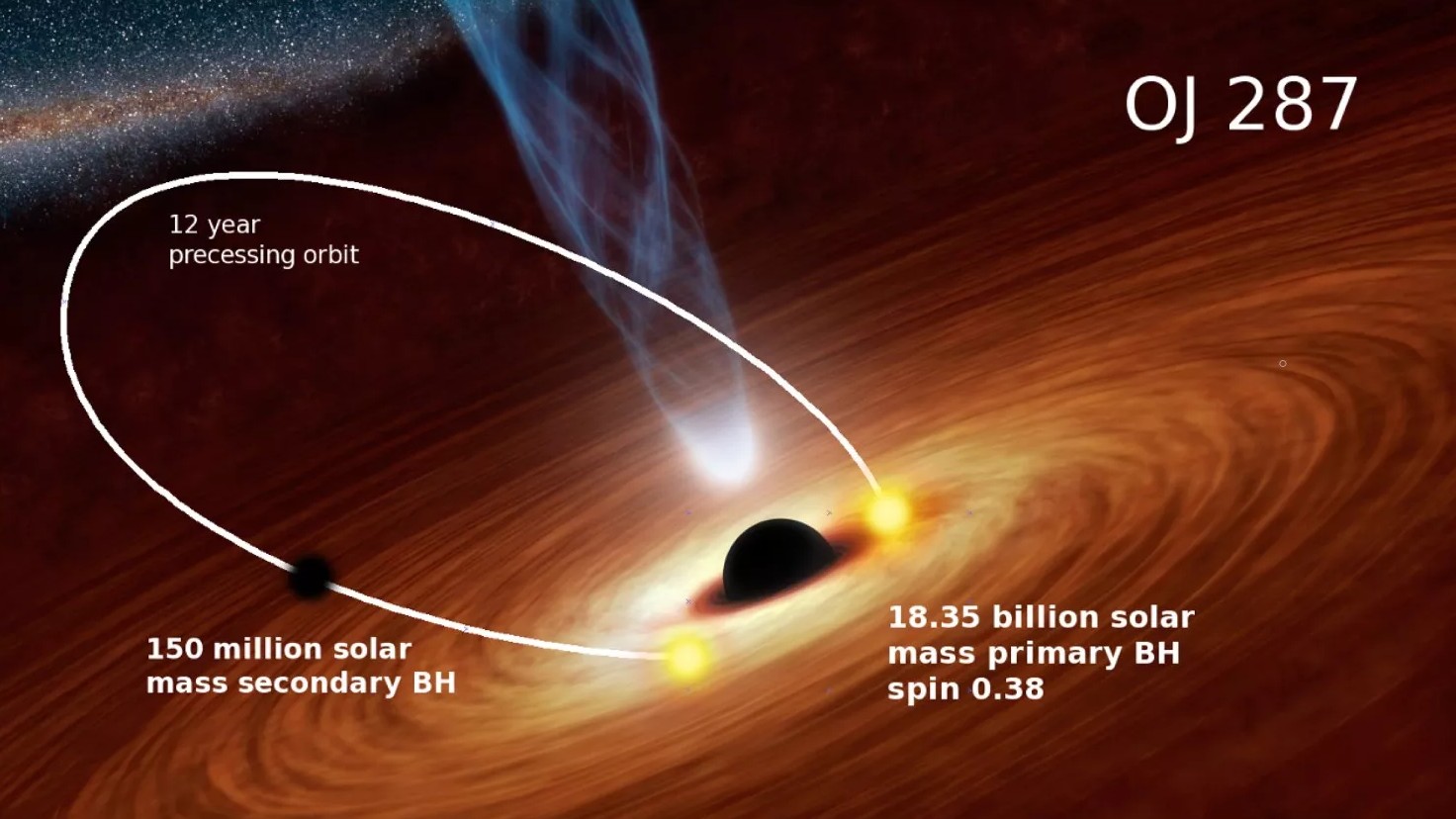
In a distant galaxy, a cosmic dance between two supermassive black holes emits periodic flashes of light.
All across the Universe, planets come in a wide variety of sizes, masses, compositions, and temperatures. And most have rain and snow.
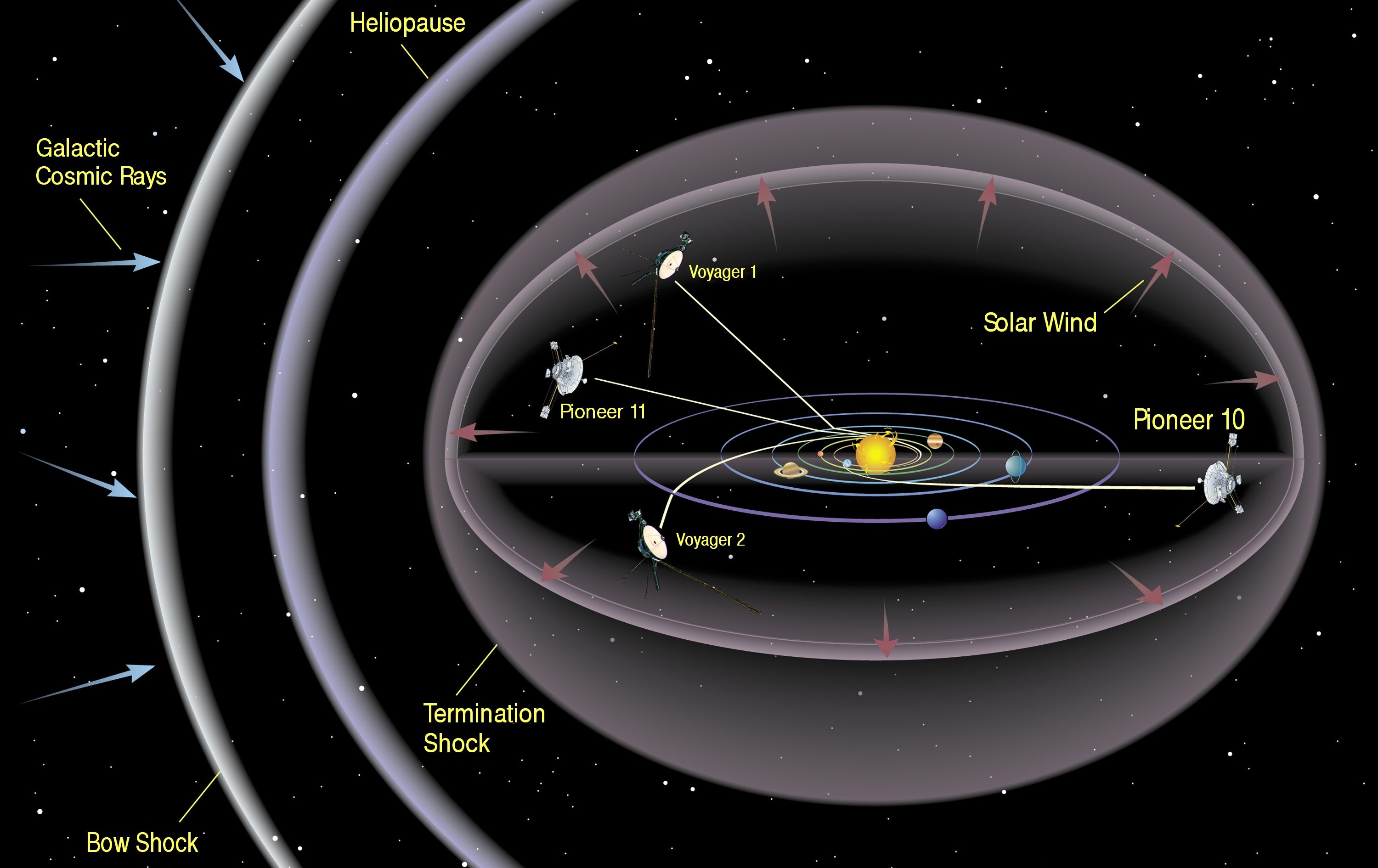
Following the advent of human space flight, NASA began naming missions after children of Zeus.
Some think the reason fundamental scientific revolutions are so rare is because of groupthink. It’s not; it’s hard to mess with success.
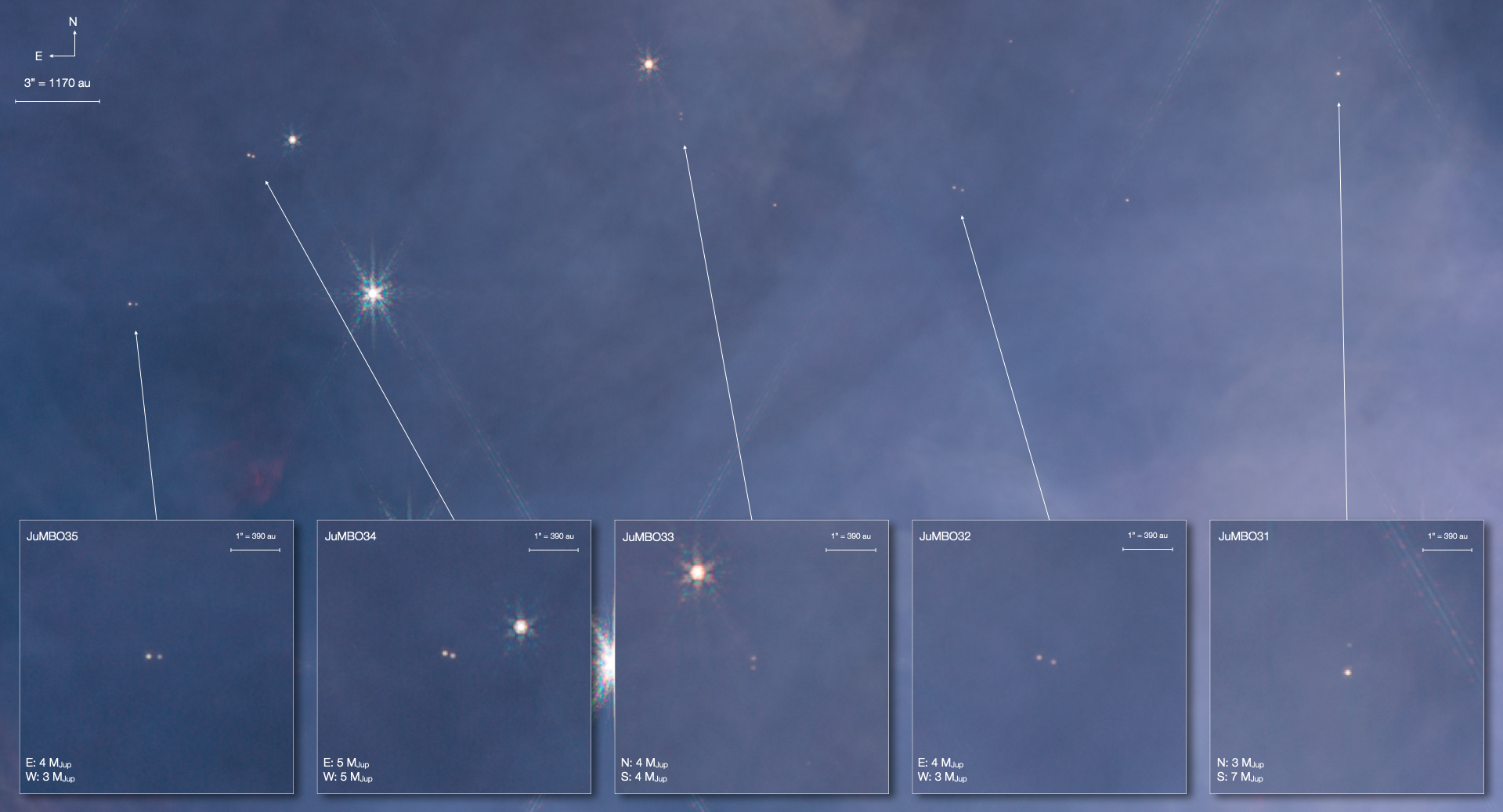
In the largest star-forming region close to Earth, JWST found hundreds of planetary-mass objects. How do these free-floating planets form?
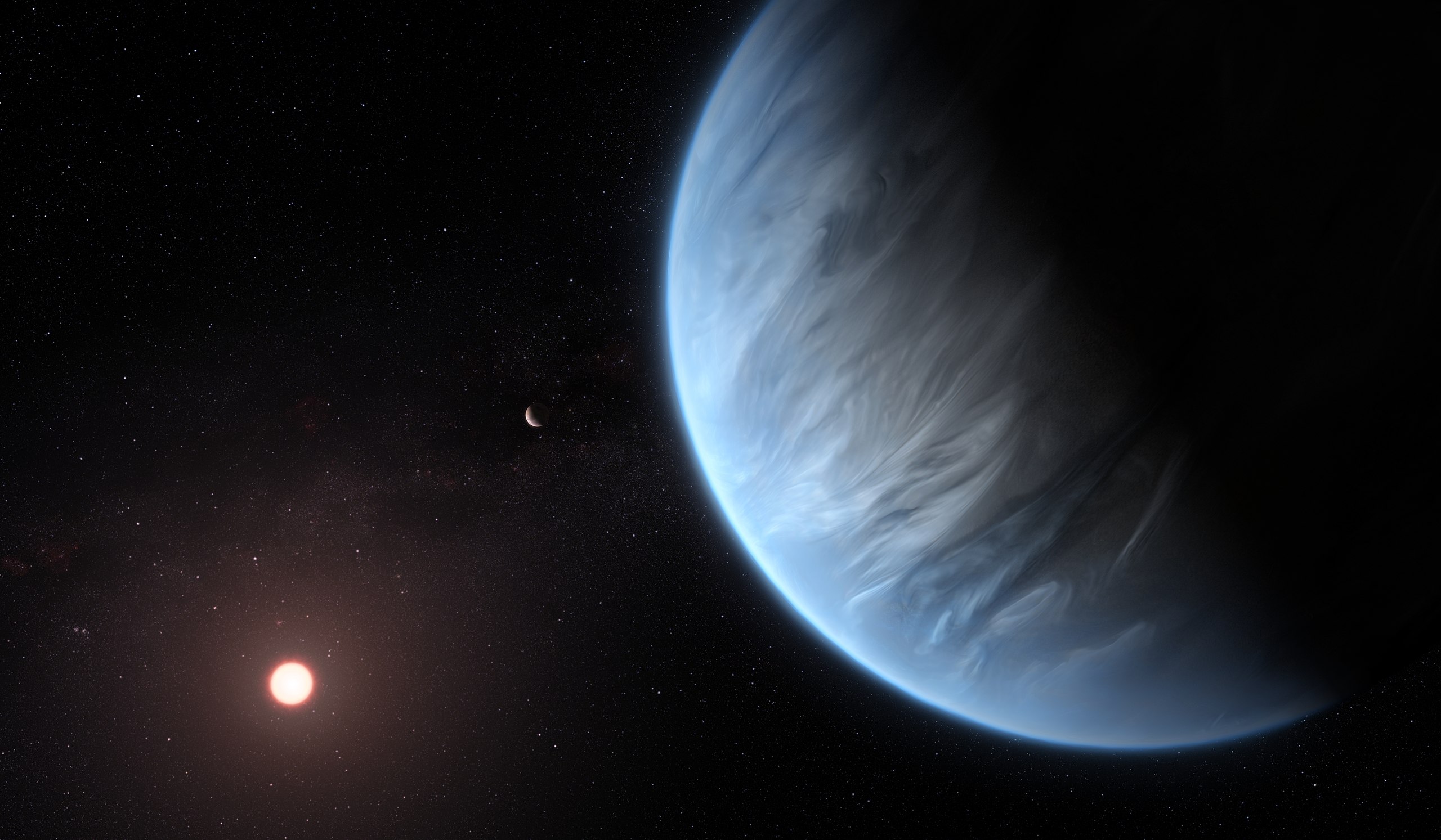
Some fascinating observations of K2-18b have come along with horrendous, speculative communications. There’s no evidence for oceans or life.
Human beings are tiny creatures compared to the 92 billion light-year wide observable Universe. How can we comprehend such large scales?
Comet A3, also known as Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS, has sprung to life since 2024’s last equinox. Here’s how to catch the show for yourself.
If the past is any guide, things are going to take off quickly.
The classic picture of Jupiter’s great rocky core might be entirely wrong.
Long before the search for biosignatures, scientists imagined a cosmos teeming with intelligent life.
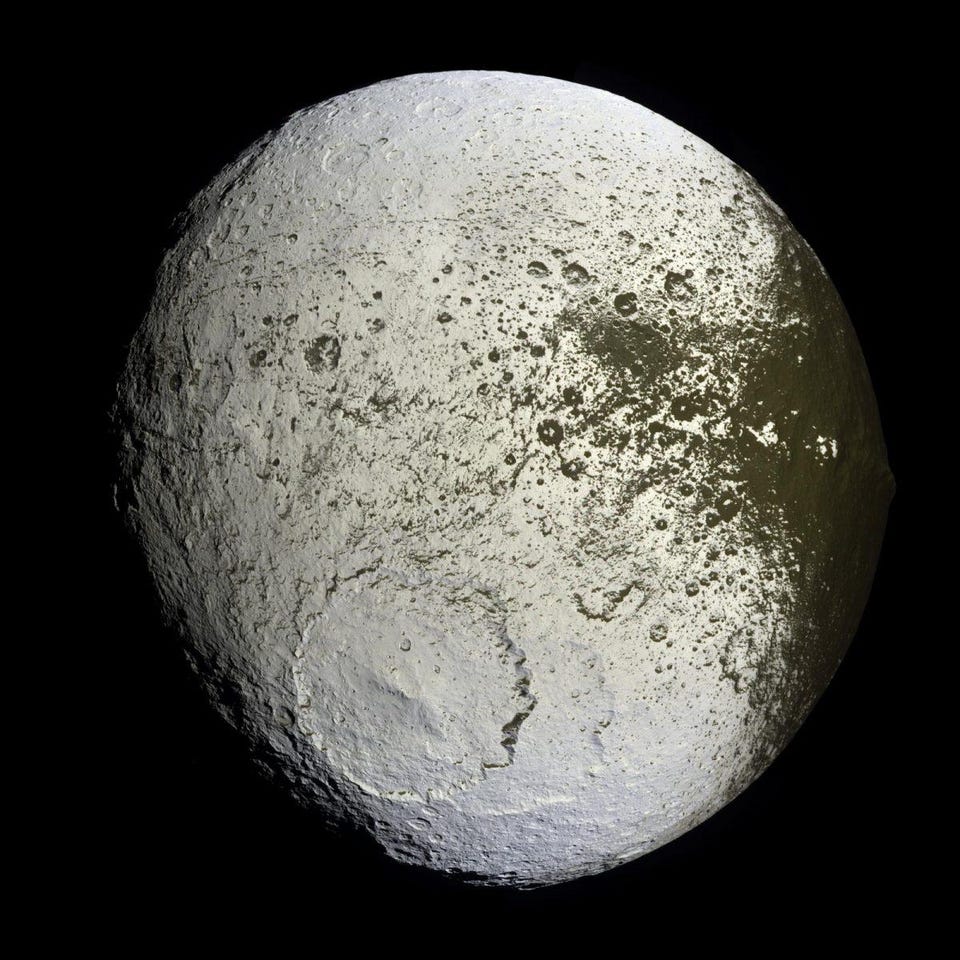
Saturn’s Iapetus, discovered way back in 1671, has three bizarre features that science still can’t fully explain.