In 2021, residents of the top America could expect to live 20.4 years longer than residents of the bottom America.
The integration of artificial intelligence into public health could have revolutionary implications for the global south—if only it can get online.
They’re in our brains, hearts, and blood — but what are they doing to us?
Could studying the Oriental hornet lead to a treatment for people with alcohol use disorder?
The findings suggest that biochemical and physical effects of exercise could help heal nerves.
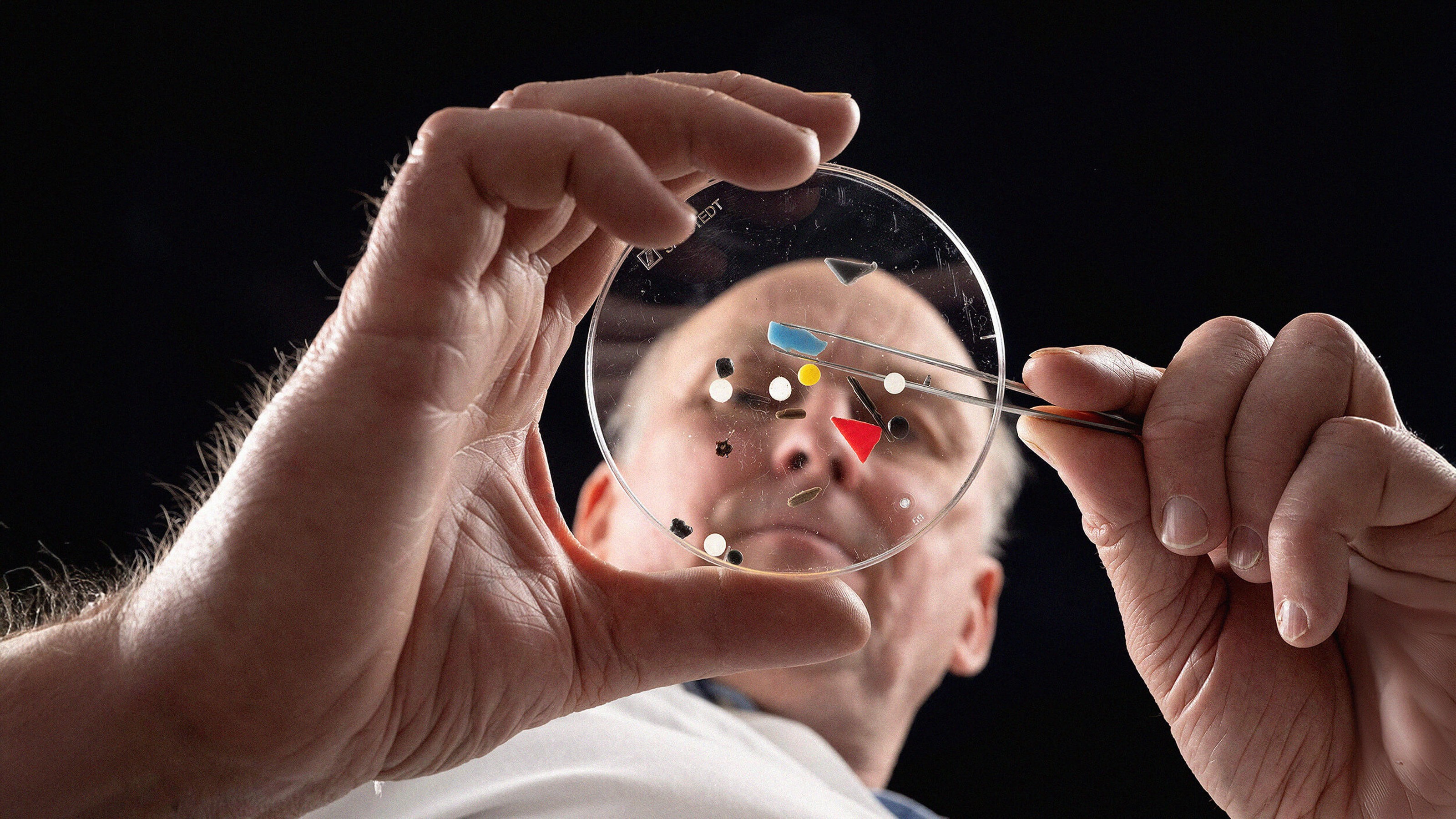
Of the millions of substances people encounter daily, health researchers have focused on only a few hundred. Those in the emerging field of exposomics want to change that.
“The field is endless, but my life is limited, as are all of ours. But you do what you can with your time,” says CSO Mart Saarma.
Some go gently into the night. Others die less prettily in freak accidents or deadly invasions, or after a showy display.
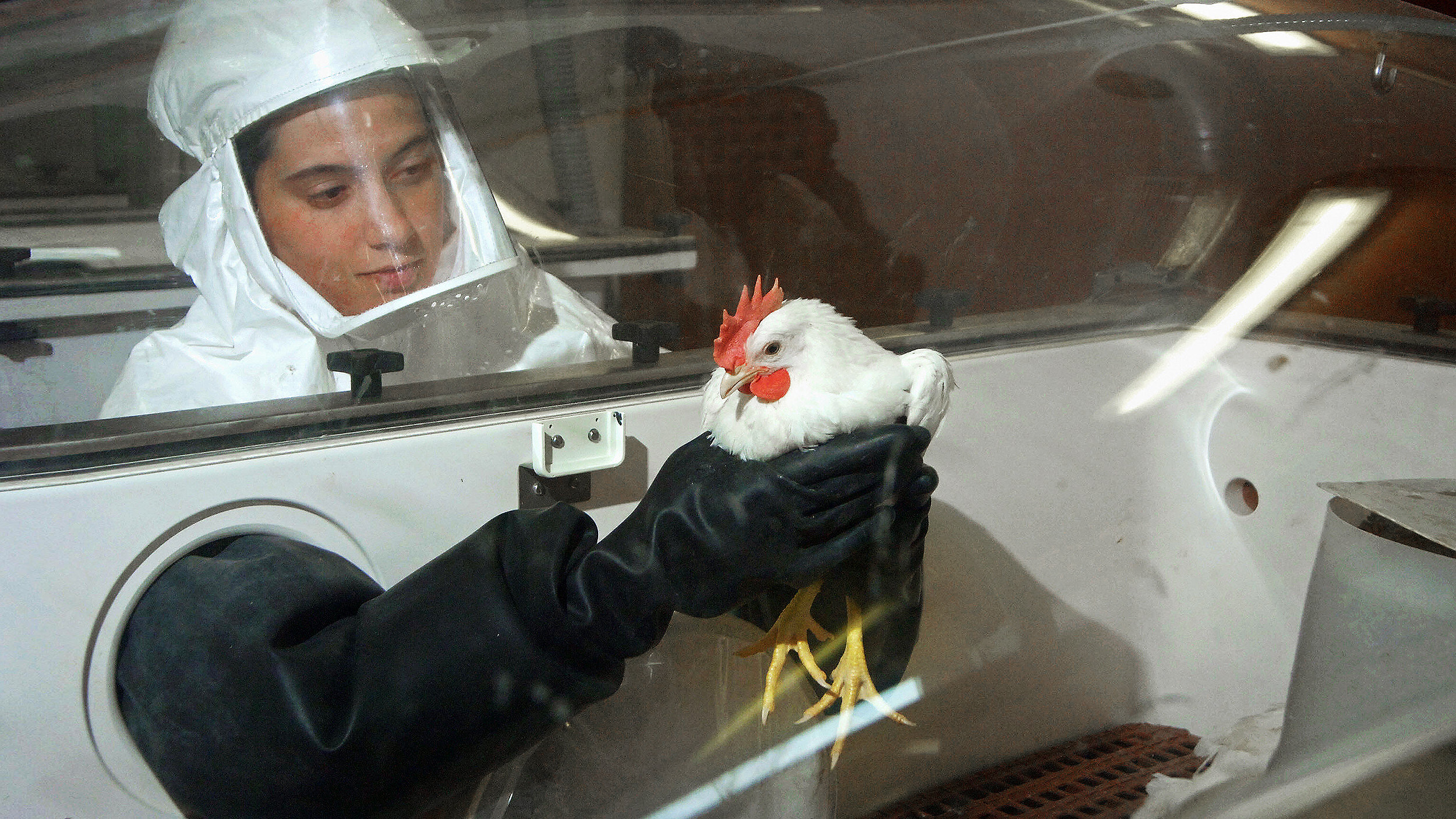
Differences in certain avian and mammalian proteins explain why avian influenza doesn’t (typically) infect humans.
“Having more stem cell activity is good for regeneration, but too much of a good thing over time can have less favorable consequences.”
Could exercise be more effective than recently approved drugs?
Propofol, a drug commonly used for general anesthesia, derails the brain’s normal balance between stability and excitability.
“Fasting…should not be demonized for simply suggesting that we take a break from eating once in a while.”
Sound may be an overlooked tool for boosting well-being.
Female physicians tend to practice medicine as it should be practiced: with care and compassion.
While GLP-1 agonists help people lose weight, different drugs could help them retain muscle at the same time.
The hangover “cures” on the market don’t work. A new hydrogel does.
GLP-1 agonists may be able to treat addiction, prevent Alzheimer’s, and more.
“If we could target those circuits very precisely, then there’s great potential to block the inflammation response for many diseases.”
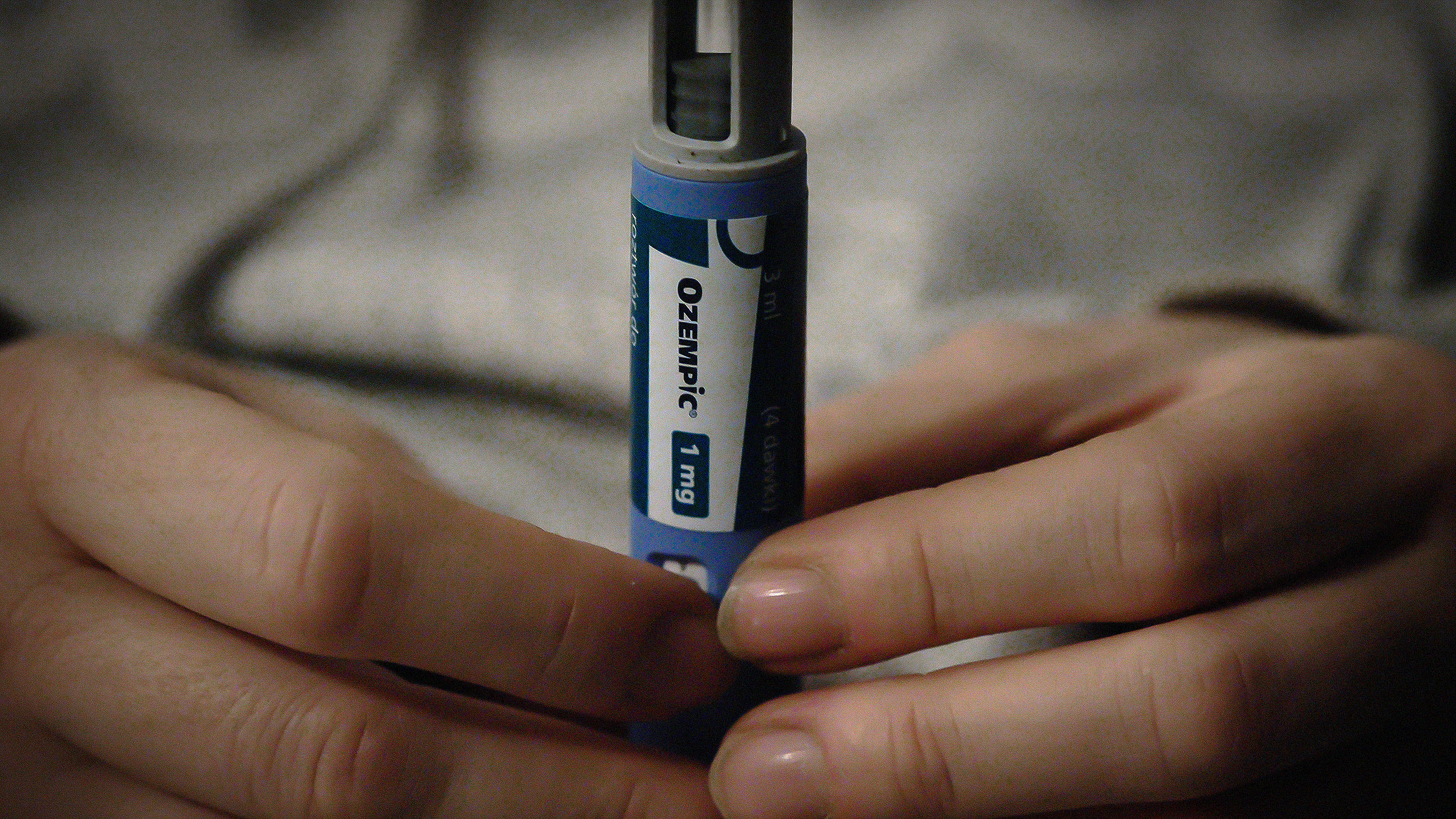
A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity.
Cancers can’t develop without genetic mutations — or can they?
Poor research can be worse than no research at all.
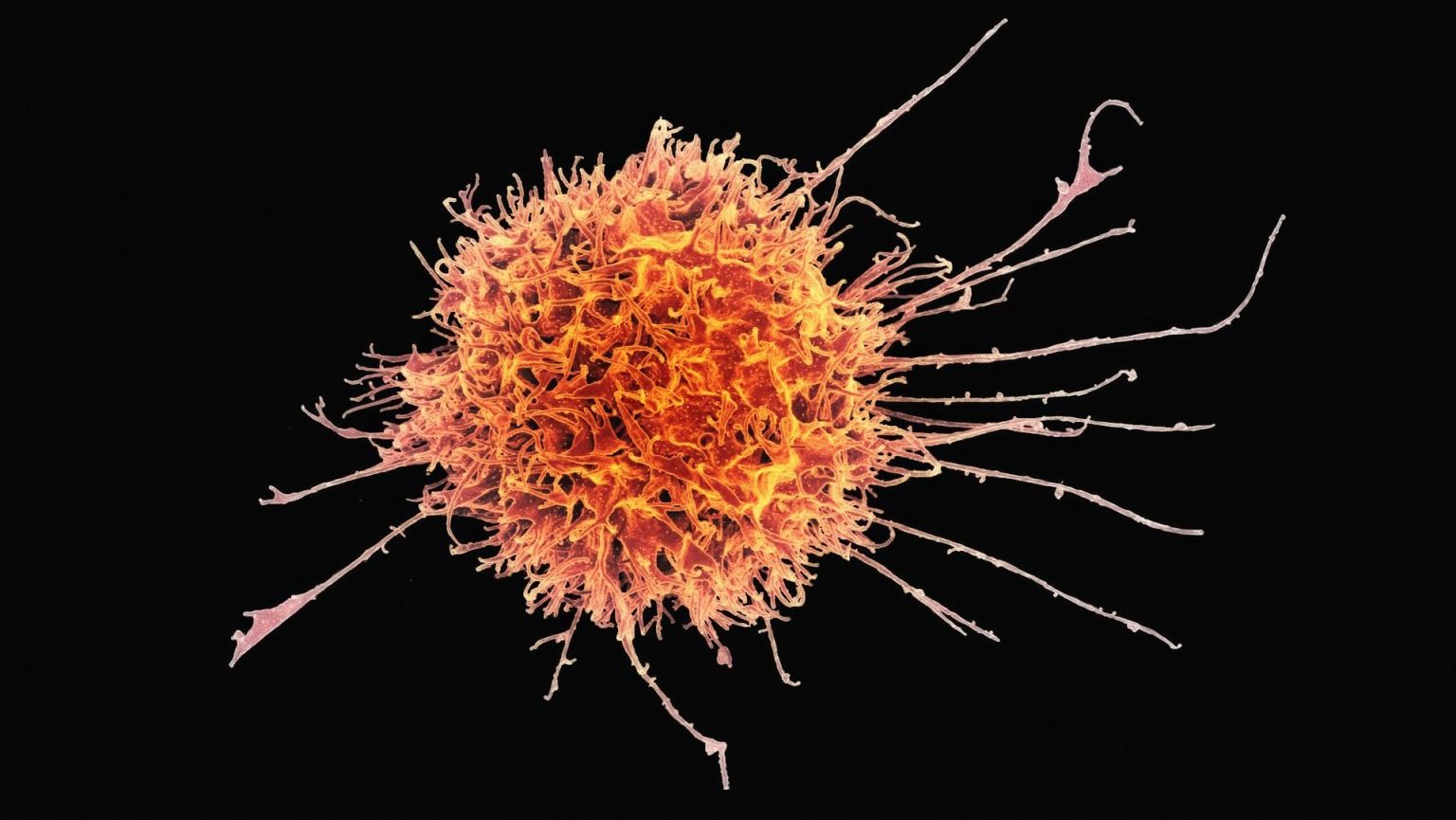
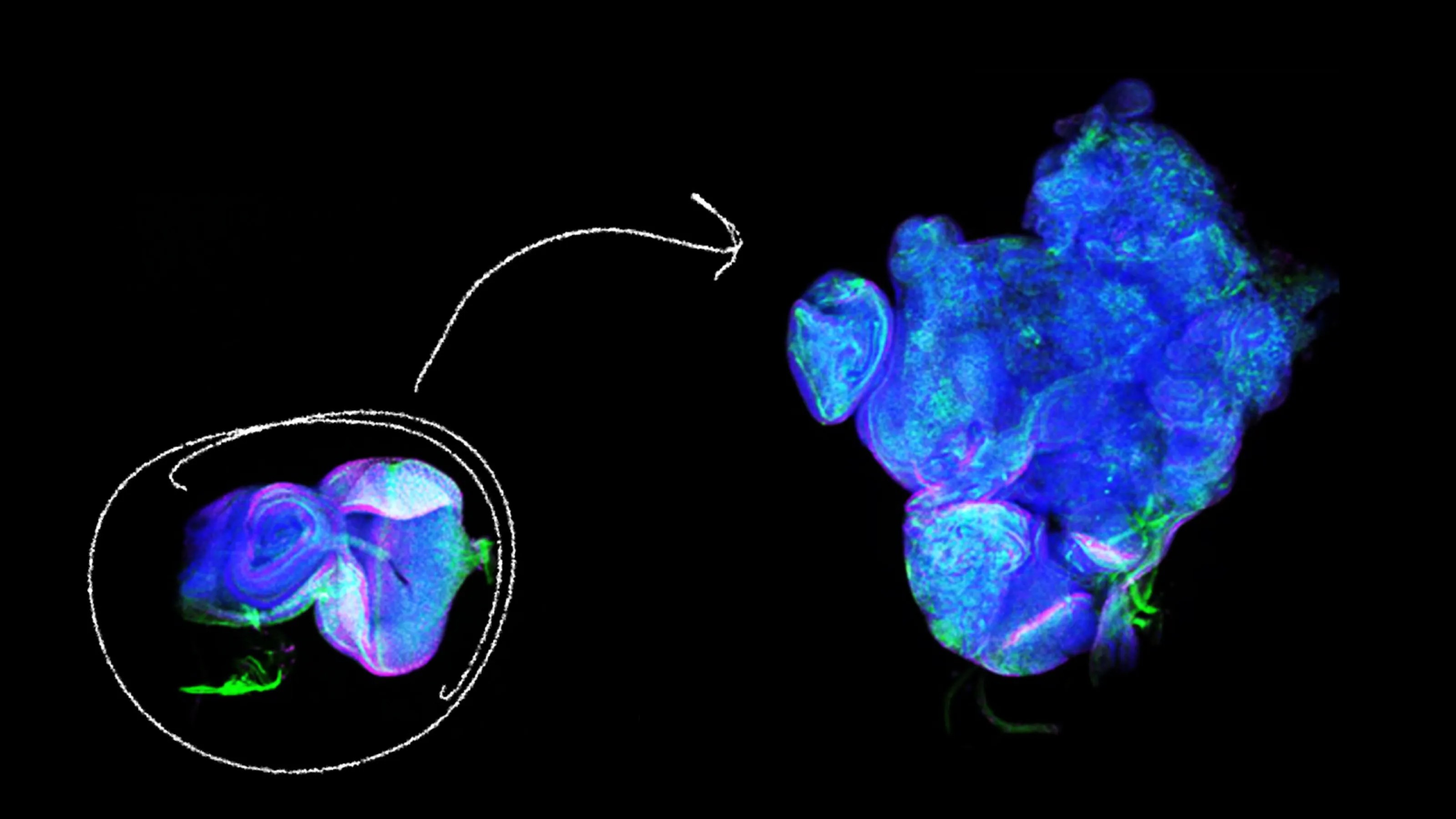
Vaccines targeting some of our deadliest cancers are showing promise in early trials.
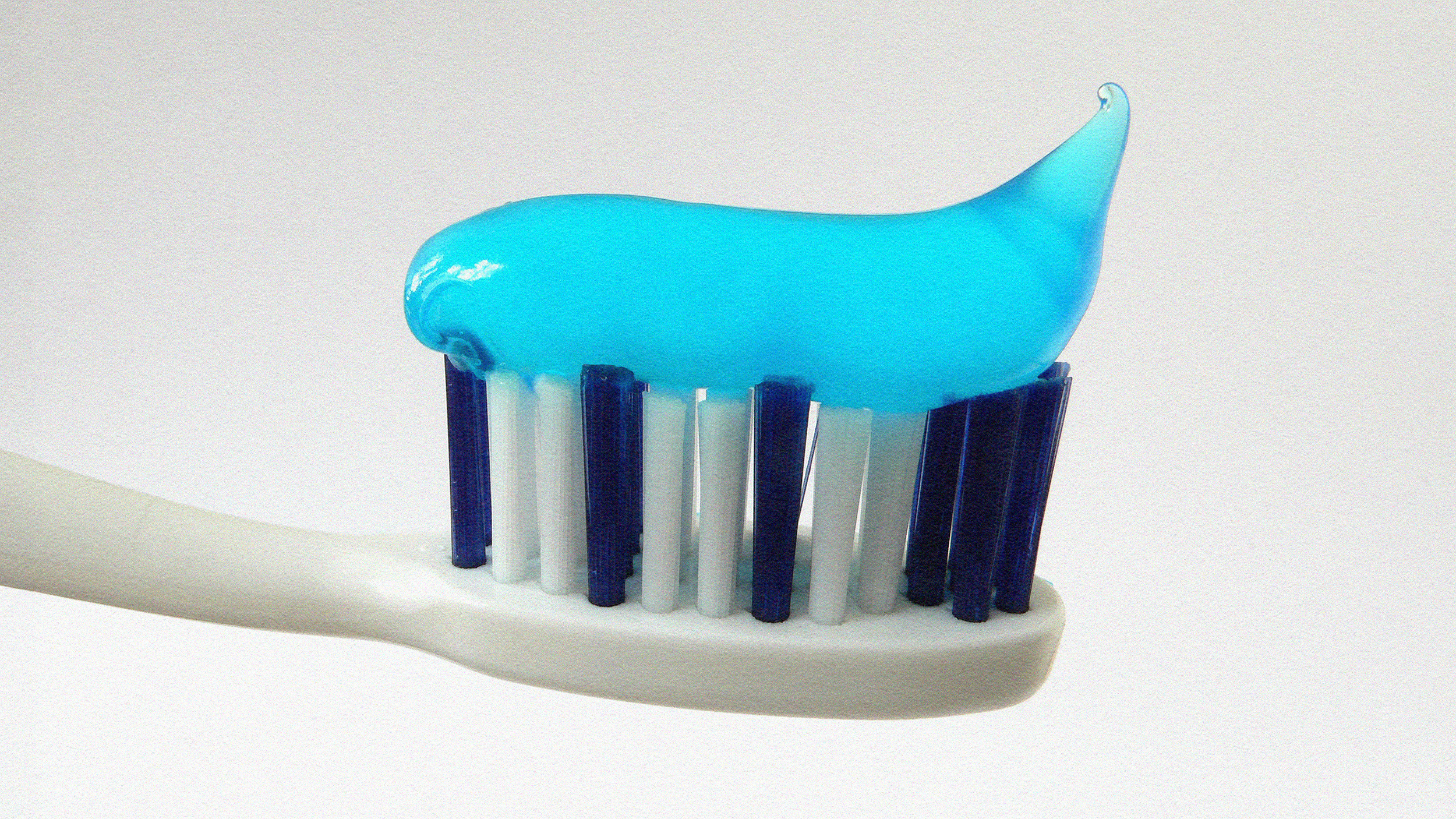
Claims circulating on the Internet — some from dentists’ websites — suggest toothpaste isn’t necessary for dental health. Is that true?
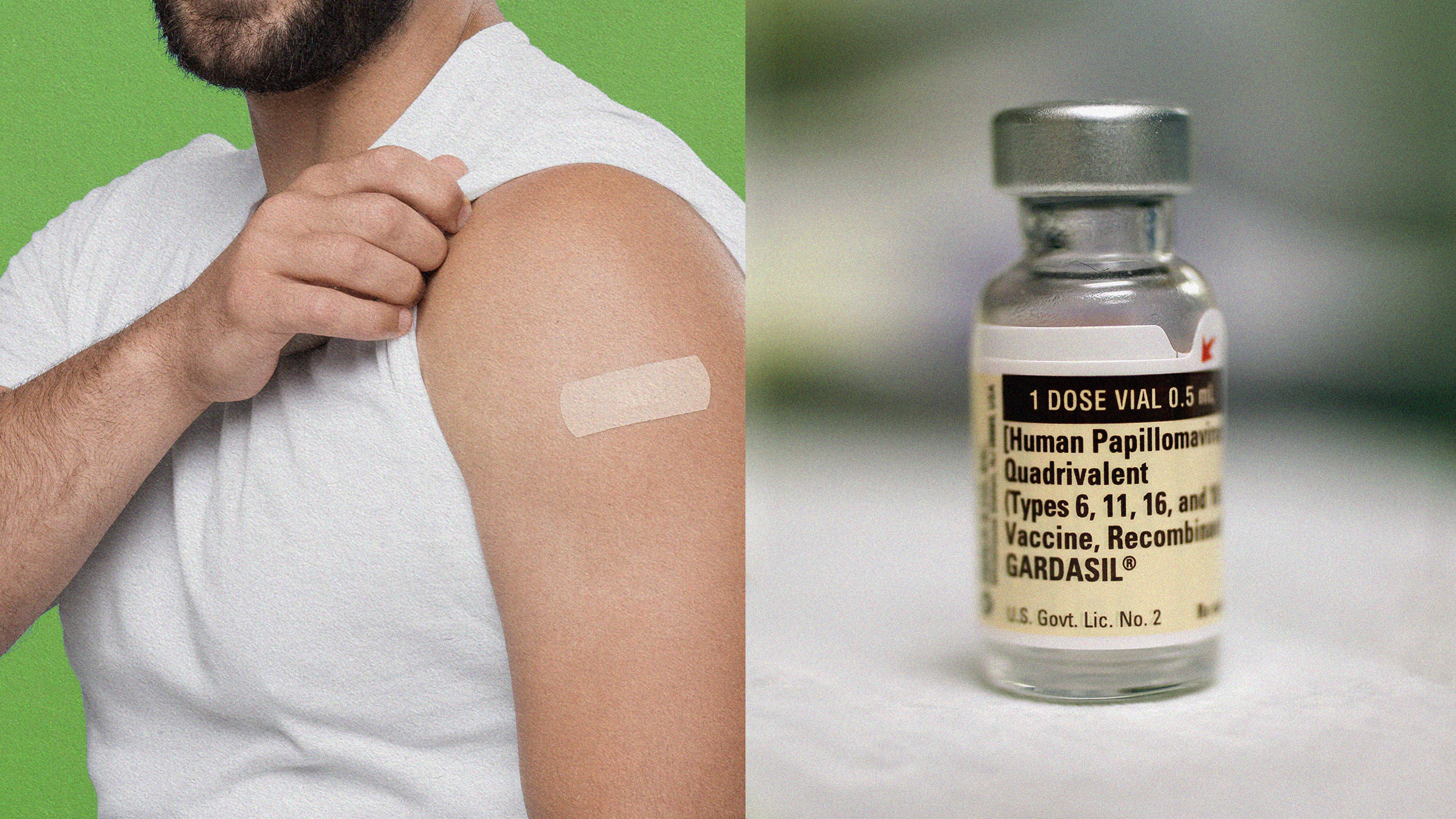
More than 90% of sexually active men will be infected with human papillomavirus in their lifetime. The virus may reduce fertility.
Susannah Fox, former chief technology officer for the HHS, explains how technology has empowered us to help fill in the cracks of the healthcare system.
More than 90% of ticks that bit treated volunteers were dead within 24 hours.
The sober reality behind the effectiveness of two new drugs touted as Alzheimer’s breakthroughs: lecanemab and donanemab.
Twin Health lets patients with diabetes see what’s happening inside their own body and can model each patient’s unique metabolism.
Long overlooked, menstrual stem cells could have important medical applications, including diagnosing endometriosis