neuroscience
When migraine and tension-headache patients overuse their medications, they can actually trigger more headaches.
Your brain may notice fearful faces, even if you don’t consciously realize it.
Instead of walking a mile in someone’s shoes, try reading a chapter in their book.
“Language is the most distinctively human talent.”
Get the most out of your coffee.
In a citizen science project, thousands of pet dogs are helping scientists to understand what happens to memory and cognition in old age.
Neuroscientist Robert Sapolsky on the science of temptation, and the limitations of your brain’s frontal cortex.
▸
6 min
—
with
Forgetfulness isn’t always a “glitch” in our memories; it can be a tool to help us make sense of the present and plan for the future.
In a study involving mice, scientists used two different techniques — one optogenetic and one pharmacologic — to recover “lost” memories.
A toxicologist explains the impacts of antidepressants on fish — and no, they’re not getting any happier.
Humans are good visual thinkers, too, but we tend to privilege verbal thinking.
Humans are musical animals four million years in the making, explained by music expert Michael Spitzer.
▸
8 min
—
with
Your breathing rhythm influences a wide range of behaviors, cognition, and emotion.
Compared to people who took a placebo, the brains of those who took caffeine pills had a temporarily smaller gray matter volume.
Creative people are better able to engage brain systems that don’t typically work together.
Researchers are looking at neurons required for touch-mediated pain relief.
Pathogenic, self-propagating proteins called prions found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s are also found in Down syndrome patients.
And it’s much, much less expensive.
Over time, different structures in the brain come to play unique roles in the storage and retrieval of long-term memories.
Solving difficult visual puzzles seems to help the brain “rewire” itself by forming new neural pathways.
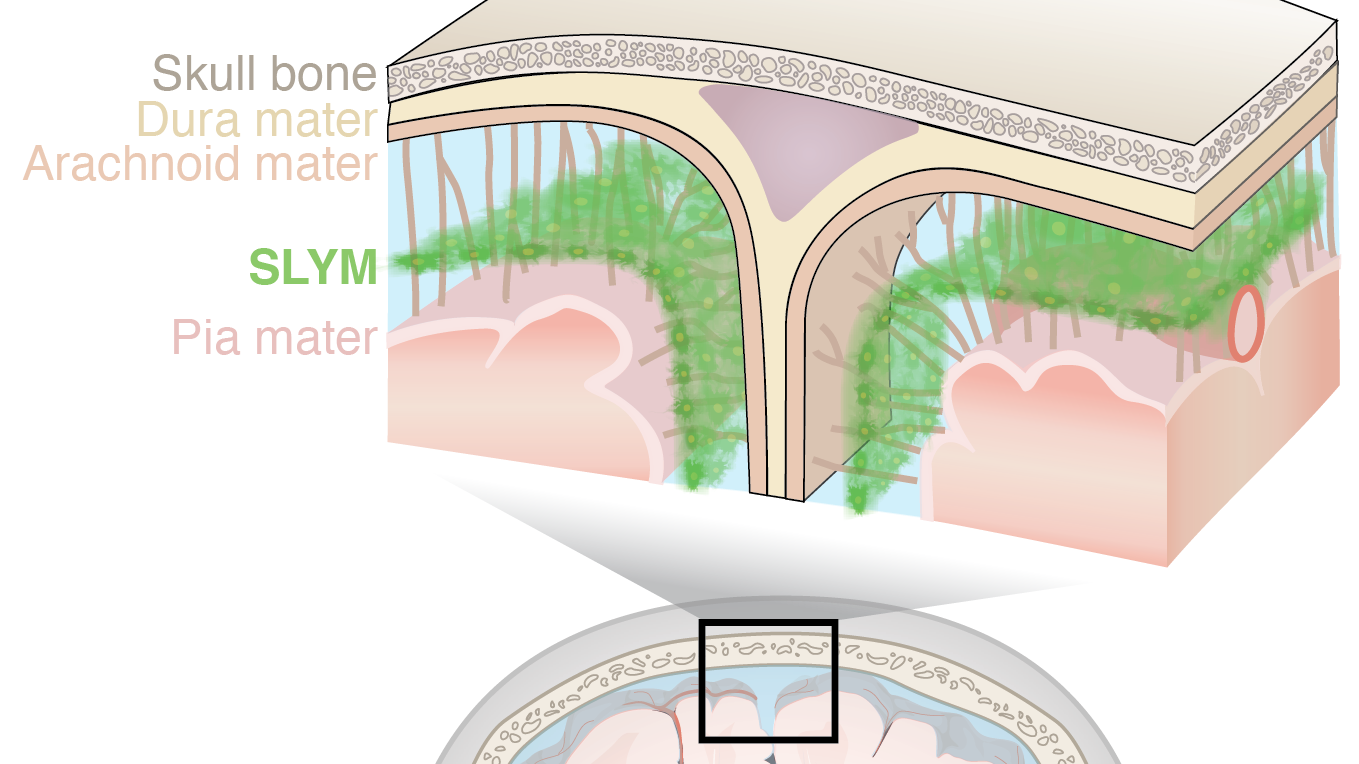
The “subarachnoidal lymphatic-like membrane” helps shield and protect the brain.
“Jumping genes” exist in various forms, including as remnants of ancient retroviruses, and make up about 45% of the human genome.
The majority of children who stutter will spontaneously recover from it without intervention, but some 20% of people do not.
Boredom isn’t the enemy; it’s a catalyst for changing your relationship to work.
Sharing food and kissing are among the signals babies use to interpret their social world, according to a new study.
They could also “turn off” their fear.
Experts explain how lie detectors work, what happens in the brain when we tell lies and how accurate polygraph tests are.
Of the world’s 300 honey varieties, none is stranger and more dangerous than mad honey.
When we’re stressed, our hormones and nervous system produce all sorts of odors.
These were the stories you clicked on the most.