human body
They’re in our brains, hearts, and blood — but what are they doing to us?
The findings suggest that biochemical and physical effects of exercise could help heal nerves.
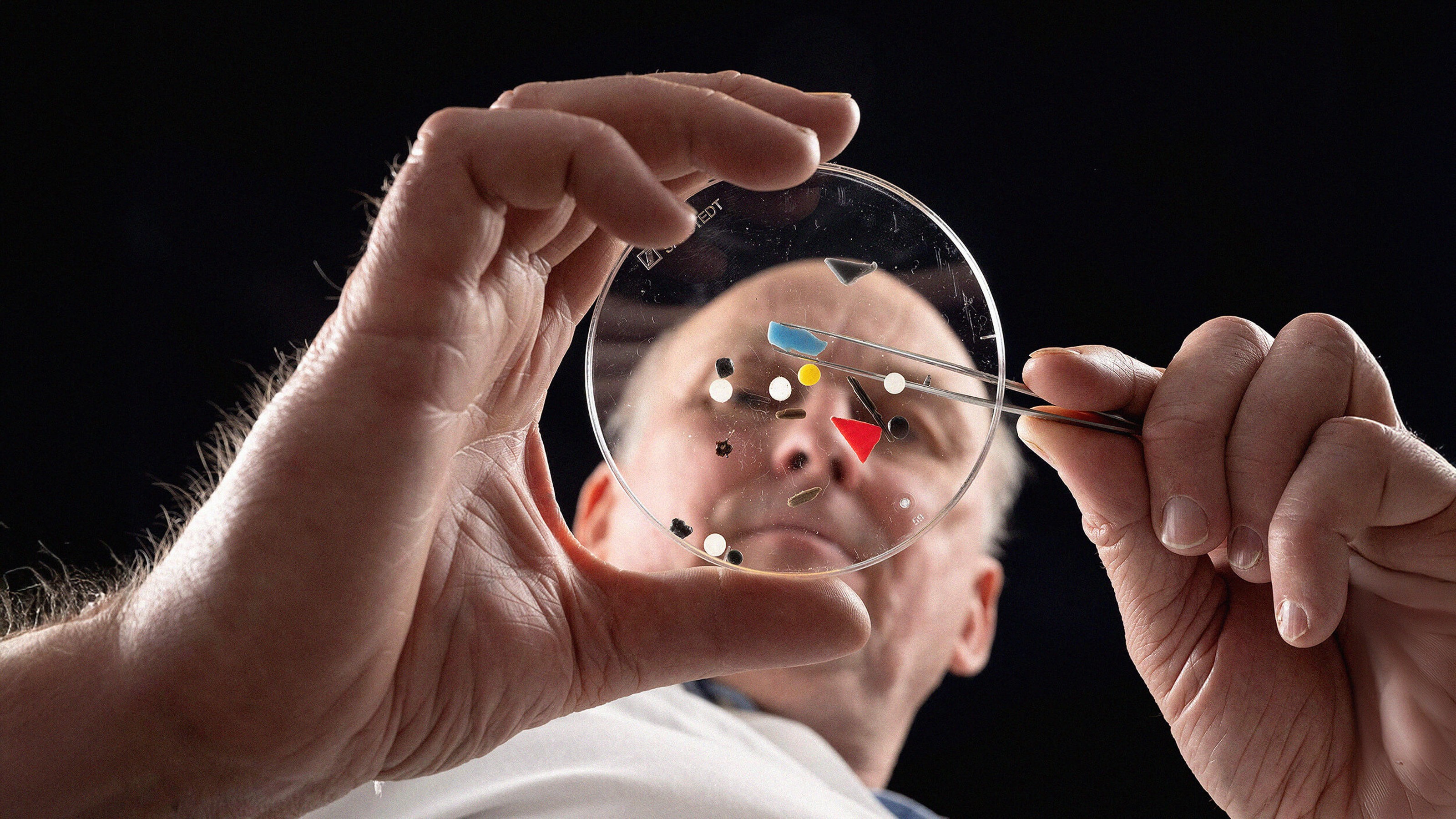
Of the millions of substances people encounter daily, health researchers have focused on only a few hundred. Those in the emerging field of exposomics want to change that.
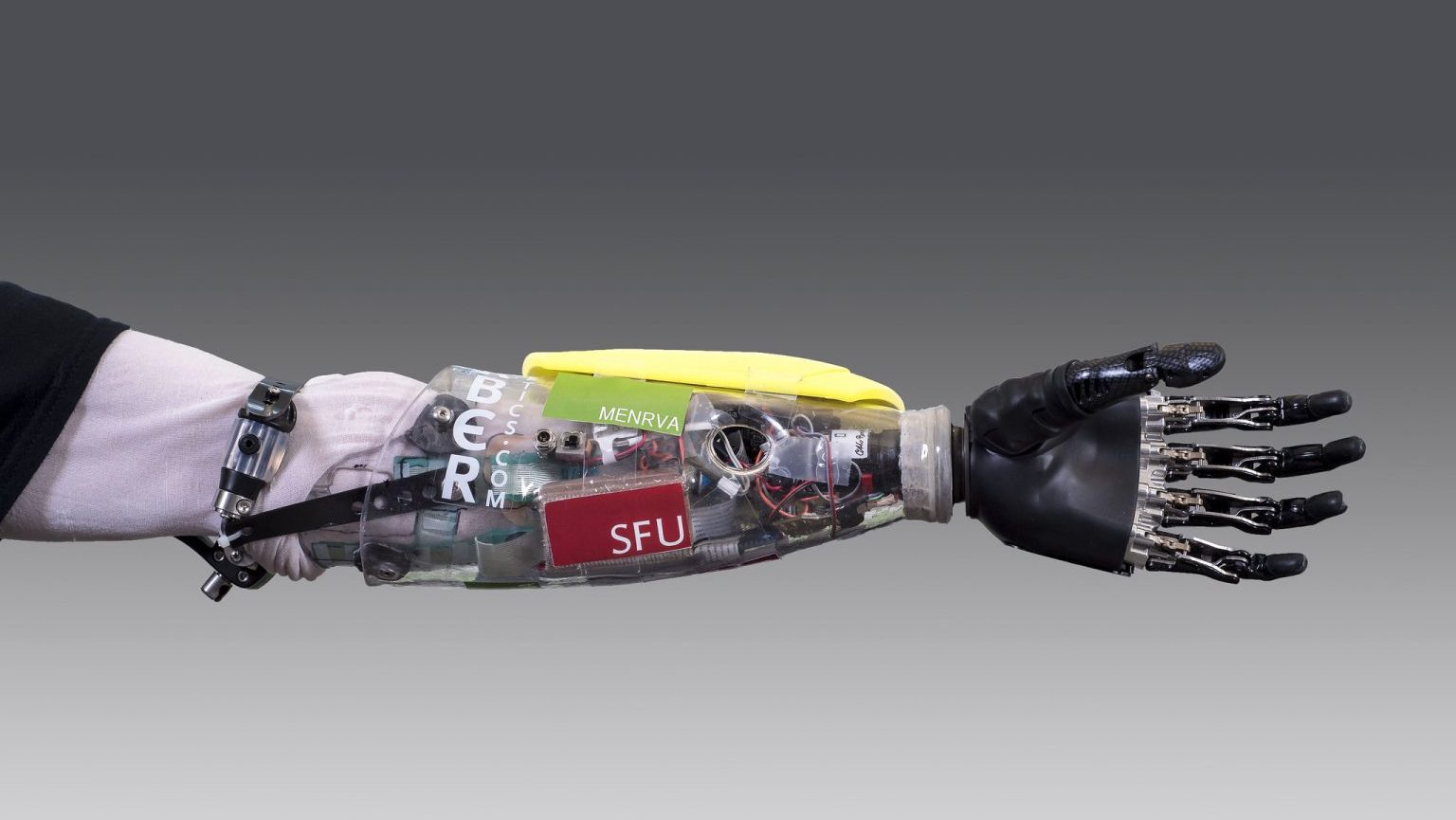
In the international competition, people with physical disabilities put state-of-the-art devices to the test as they race to complete the tasks of everyday life.
Whether your hair is straight, wavy, curly, or kinky isn’t just genetic in nature. It depends on the physics of your hair’s very atoms.
“The field is endless, but my life is limited, as are all of ours. But you do what you can with your time,” says CSO Mart Saarma.
Some go gently into the night. Others die less prettily in freak accidents or deadly invasions, or after a showy display.
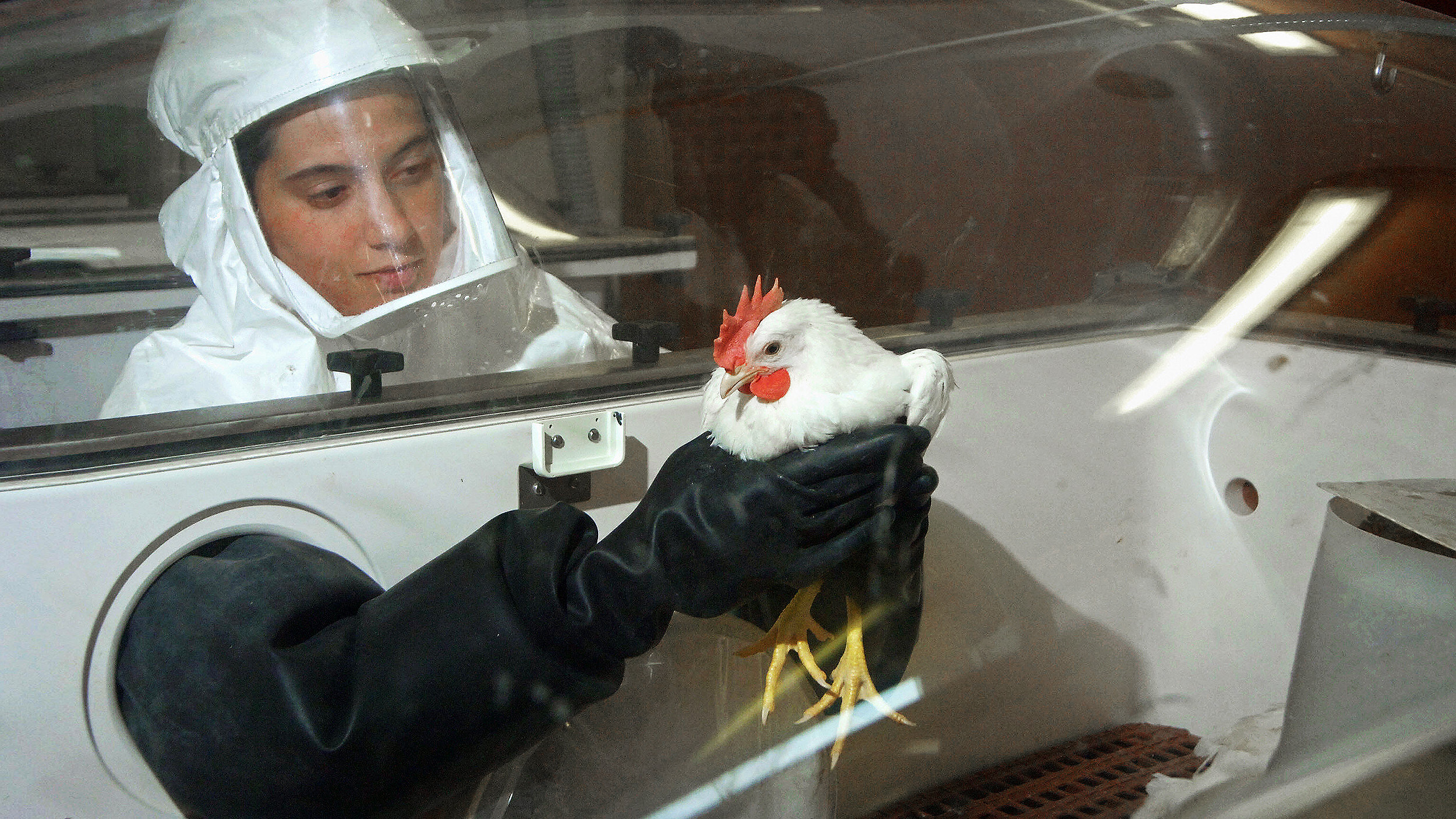
Differences in certain avian and mammalian proteins explain why avian influenza doesn’t (typically) infect humans.
“Having more stem cell activity is good for regeneration, but too much of a good thing over time can have less favorable consequences.”
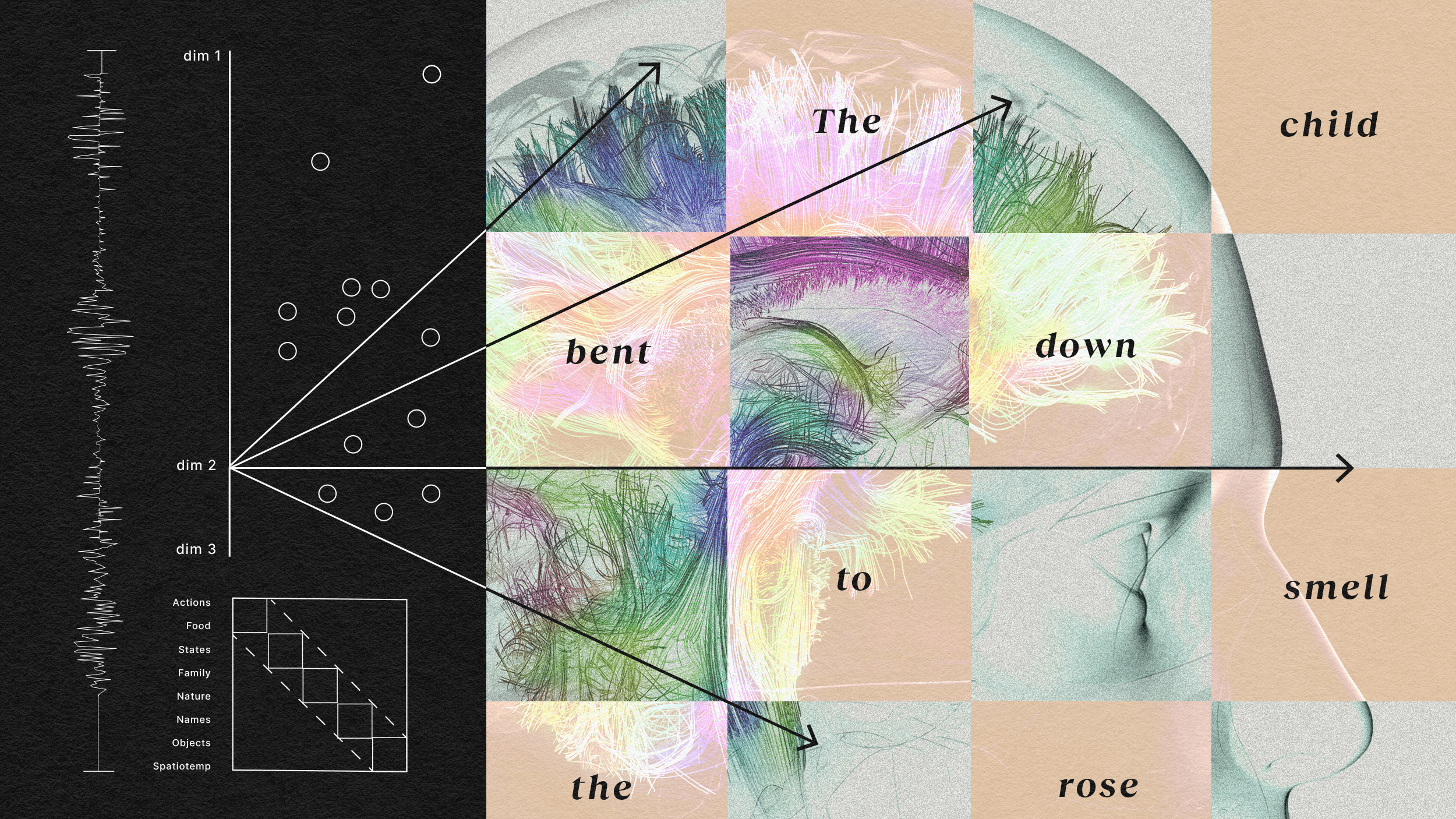
The findings show that even small areas in the brain may have the potential to represent complex meanings.
Propofol, a drug commonly used for general anesthesia, derails the brain’s normal balance between stability and excitability.
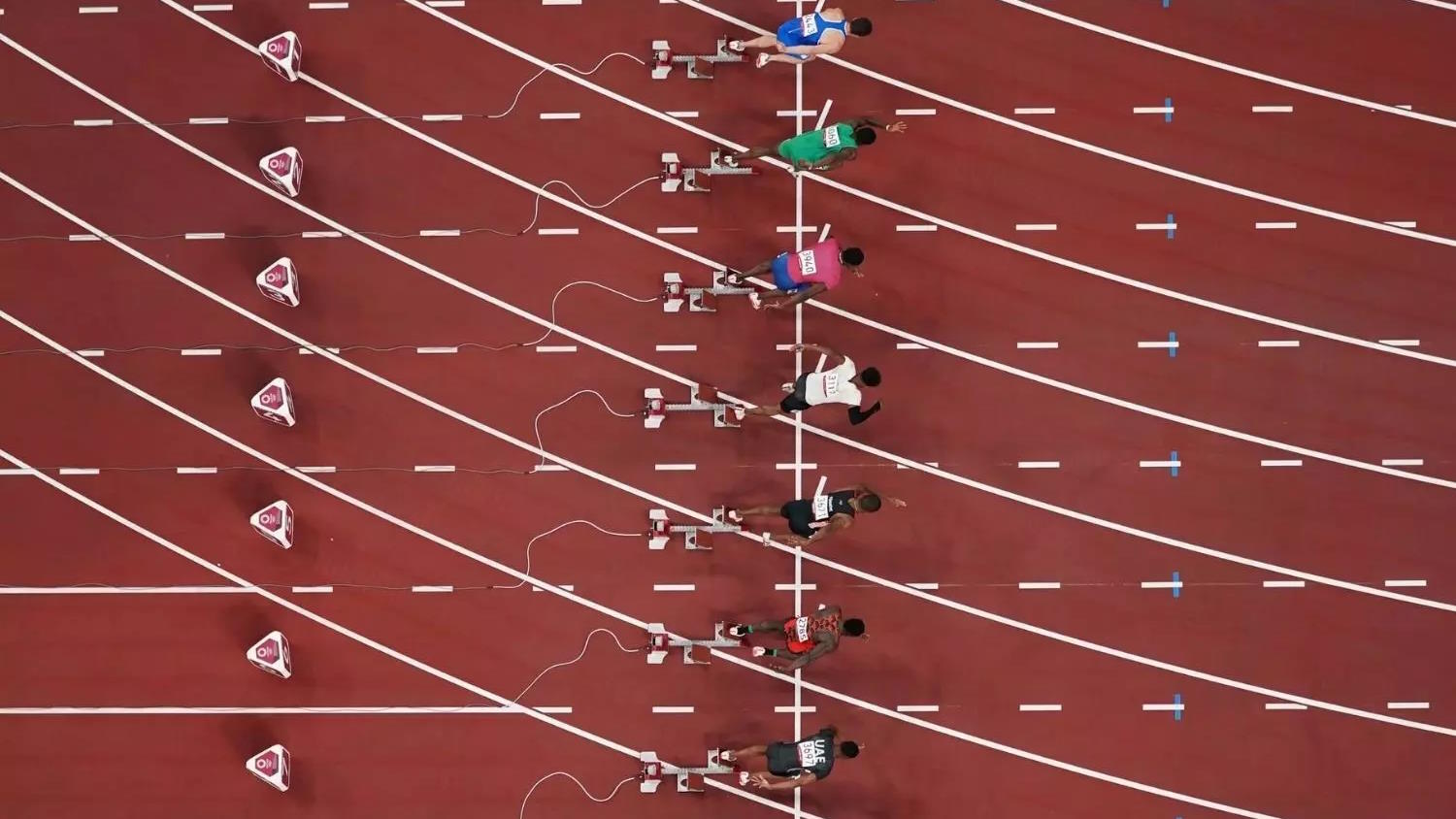
The all-time record is Usain Bolt’s 9.58 seconds, set in 2009. What is the fastest time, ultimately, for an ideal human body?
Big Think Business columnist Eric Markowitz prefaces his new series on long-term thinking with the experience that almost cut his life short.
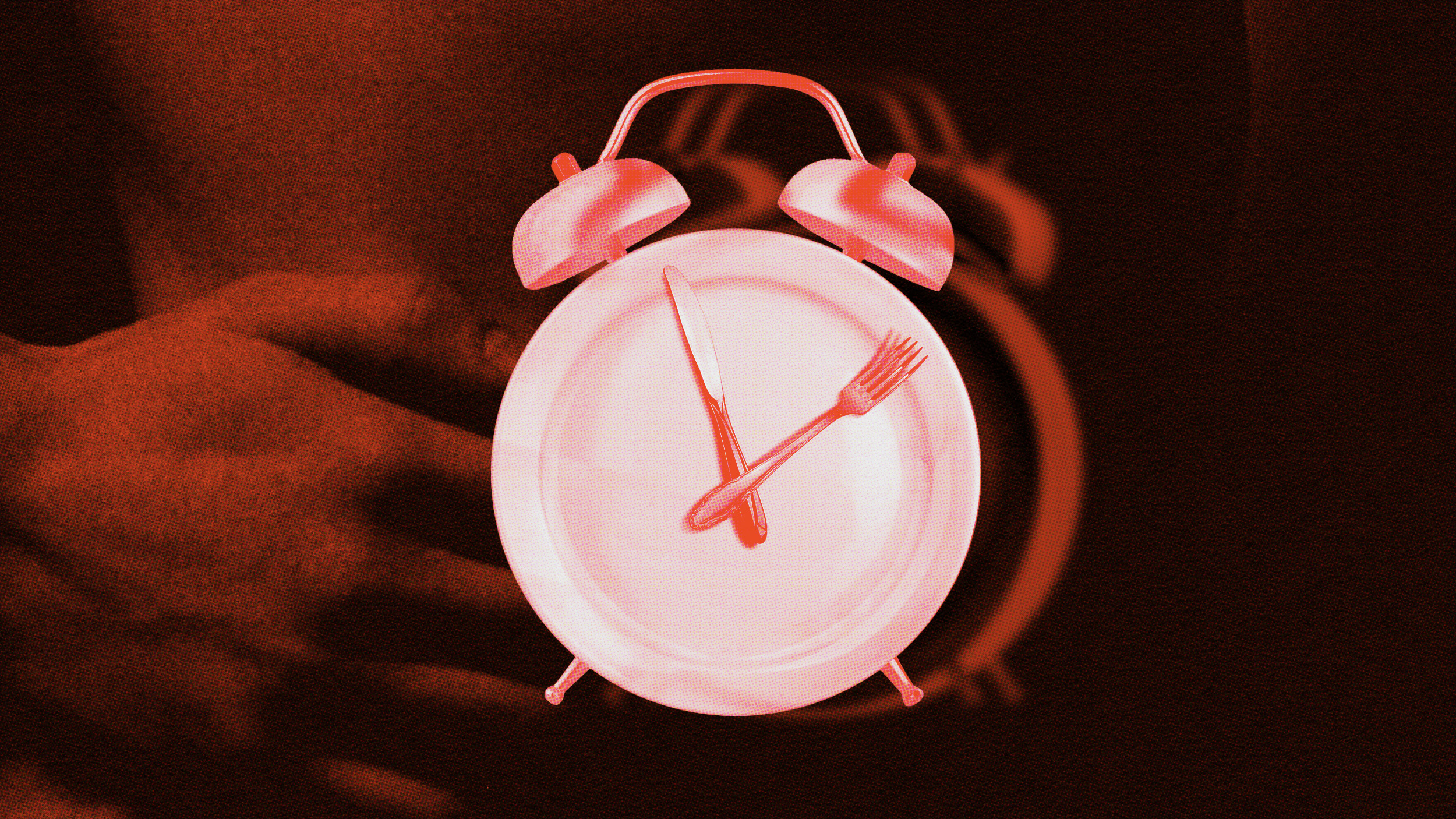
“Fasting…should not be demonized for simply suggesting that we take a break from eating once in a while.”
Cody Delistraty explores if laughter can help alleviate the physical symptoms of grief.
An excerpt from renowned neuropsychologist Nicholas Humphrey’s book “Sentience: The Invention of Consciousness.”
Depression can cause you to think too much — and physically sense too little.
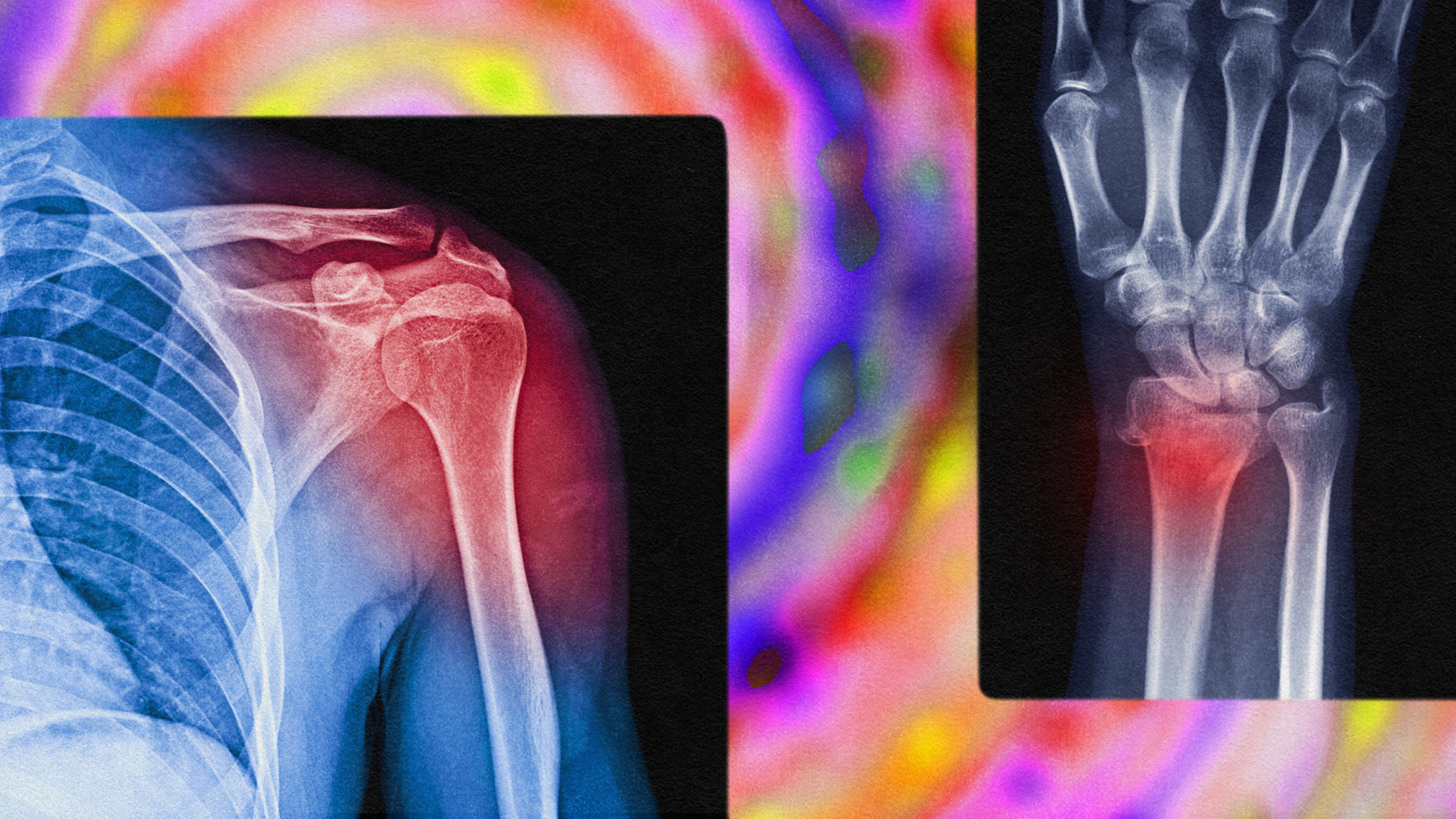
Fixing chronic pain in the body may sometimes require a treatment focused on the brain.
SARS-CoV-2 first emerged in humans in 2019. Despite much noise generated by lab leak proponents, the evidence indicates a natural origin.
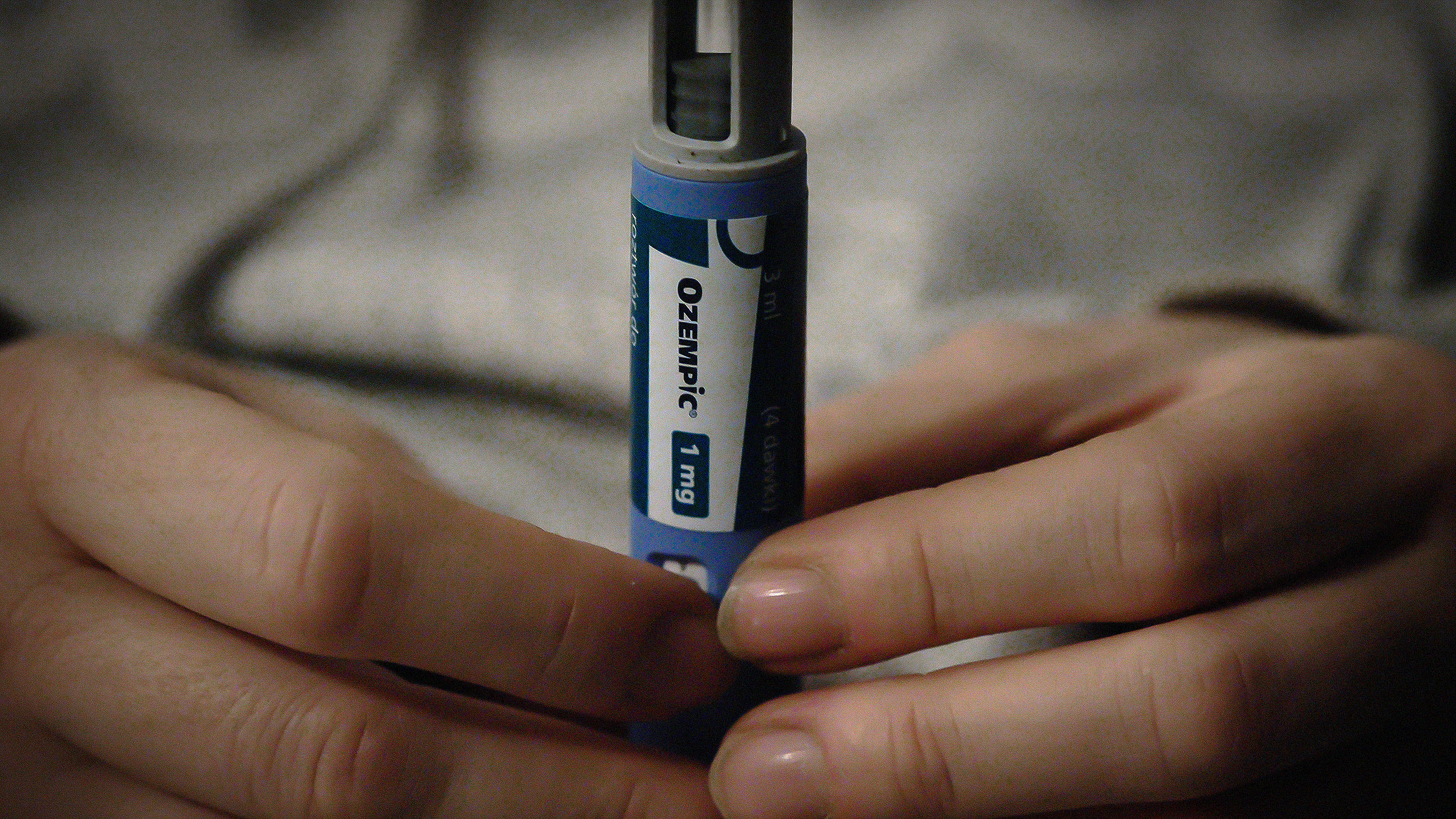
While GLP-1 agonists help people lose weight, different drugs could help them retain muscle at the same time.
The hangover “cures” on the market don’t work. A new hydrogel does.
GLP-1 agonists may be able to treat addiction, prevent Alzheimer’s, and more.
“If we could target those circuits very precisely, then there’s great potential to block the inflammation response for many diseases.”
A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity.
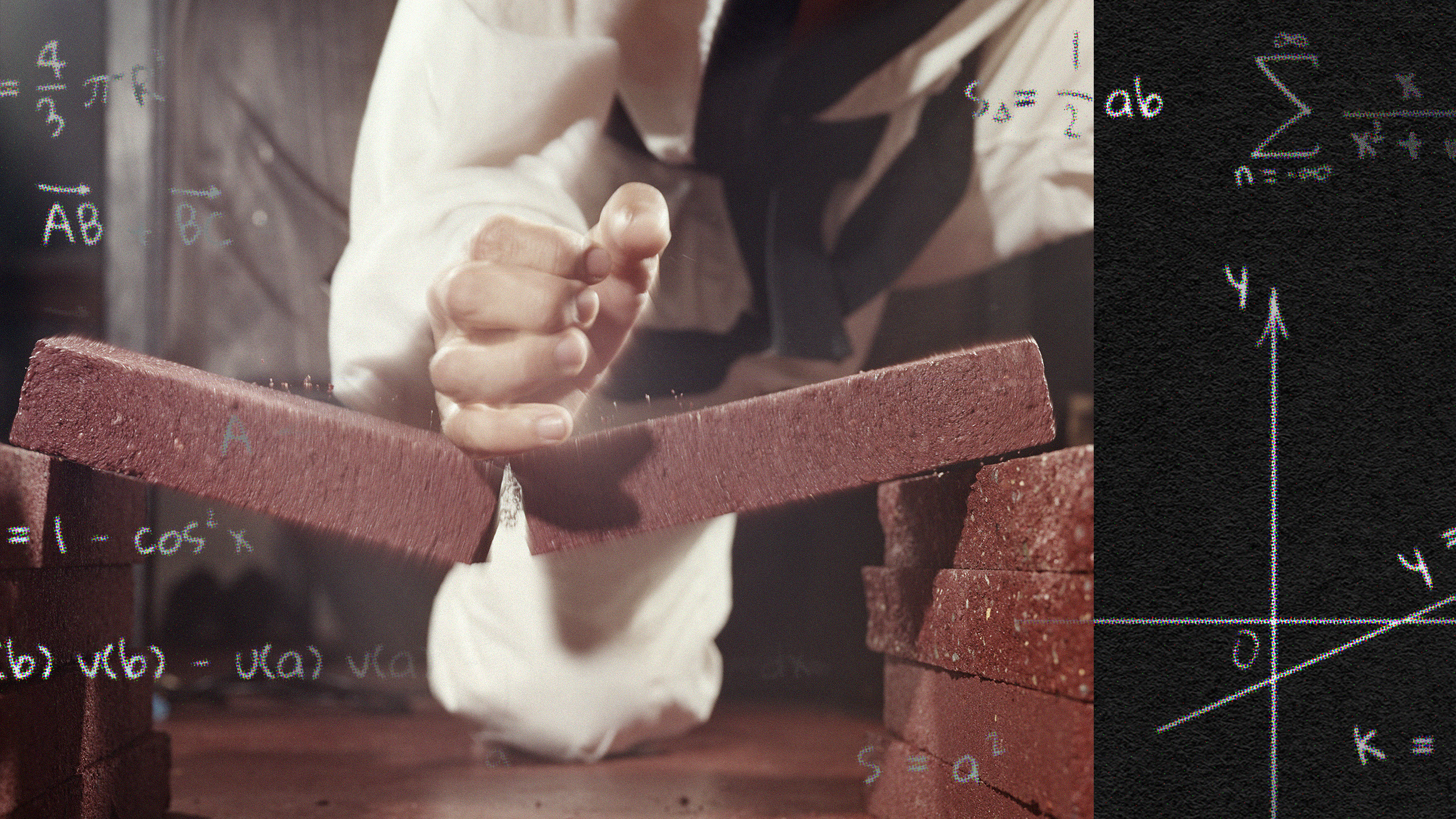
A human hand has the power to split wooden planks and demolish concrete blocks. A trio of physicists investigated why this feat doesn’t shatter our bones.
Even with the best technology imaginable, you’d probably never be able to exist as a consciously aware brain in a vat.
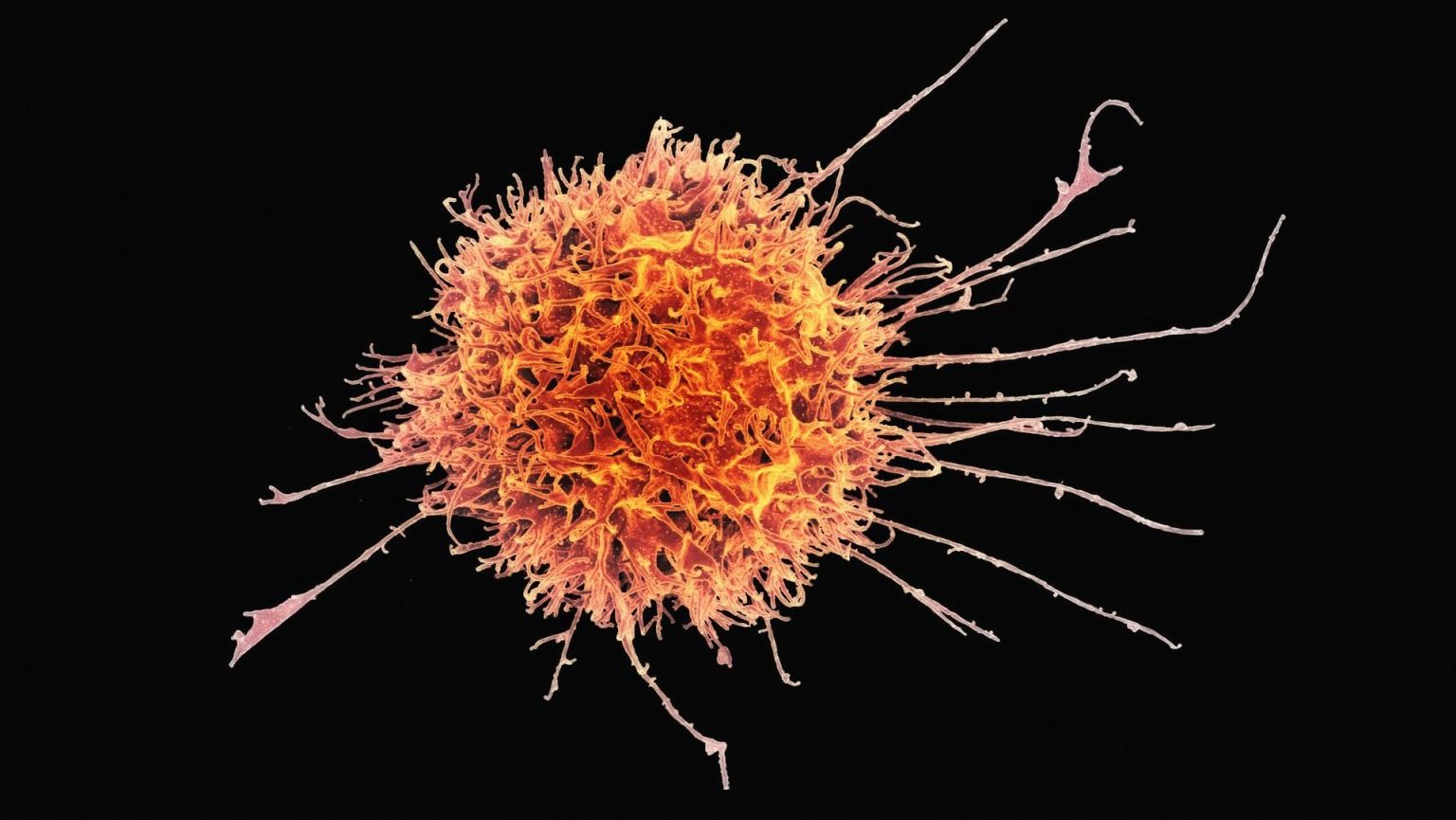
Vaccines targeting some of our deadliest cancers are showing promise in early trials.
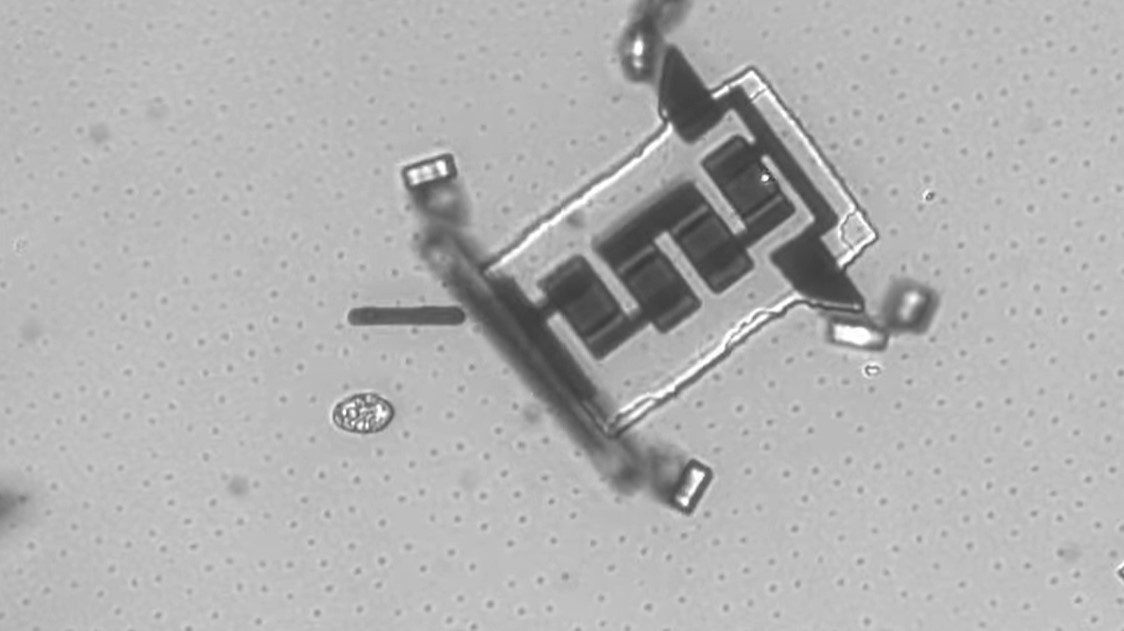
What would it take to create a truly intelligent microbot, one that can operate independently?
Forensics has reached the final frontier, and could be used to solve future space accidents—or crimes.
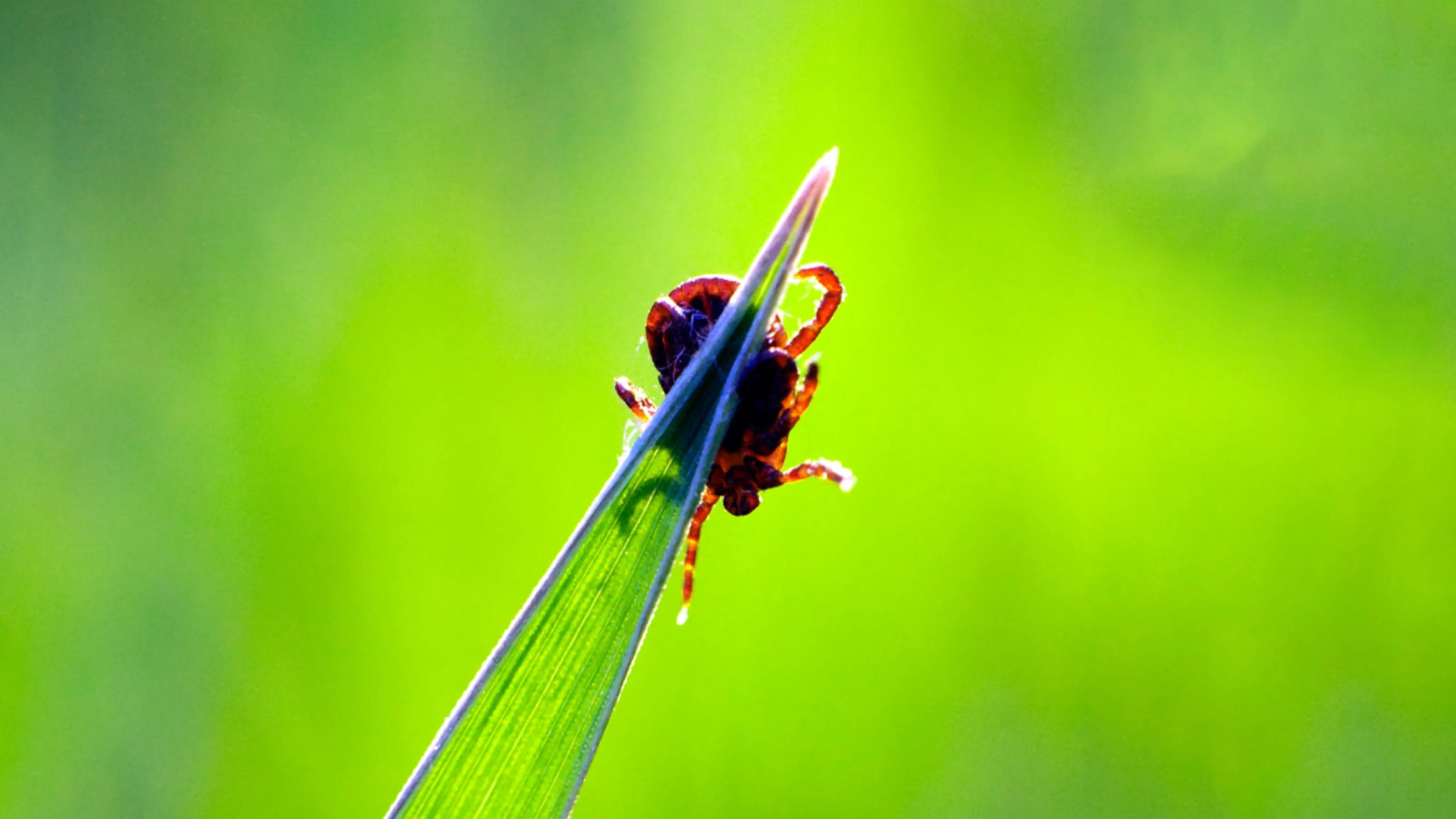
More than 90% of ticks that bit treated volunteers were dead within 24 hours.