How Christians co-opted the winter solstice

Saturnalia by Antoine Callet
- Christmas was heavily influenced by the Roman festival of Saturnalia.
- The historical Jesus was not born on December 25th as many contemporary Christians believe.
- Many staple Christmas traditions predated the festival and were tied into ancient pagan worship of the sun and related directly to the winter solstice.
In the depths of darkness covering the entire Northern Hemisphere, the winter solstice has marked the shortest day of the year. It has always held significance in many culture’s religious festivities and holidays. A great deal of religions have made the celestial moment a holy day. It is the darkest day of the whole year and for the ancients that meant a lot more to them then it does to us today. Sun worshippers and pagans have venerated this natural cycle for millennia.
Christmas as we know it today is a relatively new holiday. Many traditional elements we associate with Christmas predate Christianity by many centuries. There is also a lot of debate as to how much corporate and commercial interests have influenced this holiday as well.
Nowadays, there’s a lot of hand waving when it comes to the Christian origins of Christmas. Inarguably, however, is the fact that the holiday’s modern iteration has been influenced by many pagan and secular festivities.

Photo credit: Ivana Djudic on Unsplash
Early human celebrations and customs during the Winter Solstice
You’ll find plenty of pagan customs in Christmas that were adopted during the early Christian spread around the Roman Empire. We can look back to both the Romans and the Celts for a whole lot of our modern day Christmas traditions.
Celts began celebrating once the winter solstice arrived and rejoiced that the days were slowly getting longer, which meant that spring and the harvest was around the corner. This was most pronounced in their holiday of Yule. Early Christians, who, at that time, were seen by many as being members of an urban cult, worked hard to try to convert and ban old Pagan customs. But the rural pagan inhabitants of those lands were not convinced. Eventually the church realized they needed to co-opt some of these traditions.
Around this time, the Church came up with the idea that Jesus Christ, their savior, was born on December 25th. In the 4th century CE, Christianity had begun to draw heavily upon Roman festival of Saturnalia. Christian leaders succeeded in transposing these festivities on to their new made-up holiday.
The first mention of the Nativity feast and other early Christmas traditions appears in a Philocalian calendar dated around 354 CE. It was because of this pagan origin that celebrating Christmas was banned by the Puritans and made illegal in Massachusetts between 1659 and 1681.

Romans during the Decadence – Thomas Couture
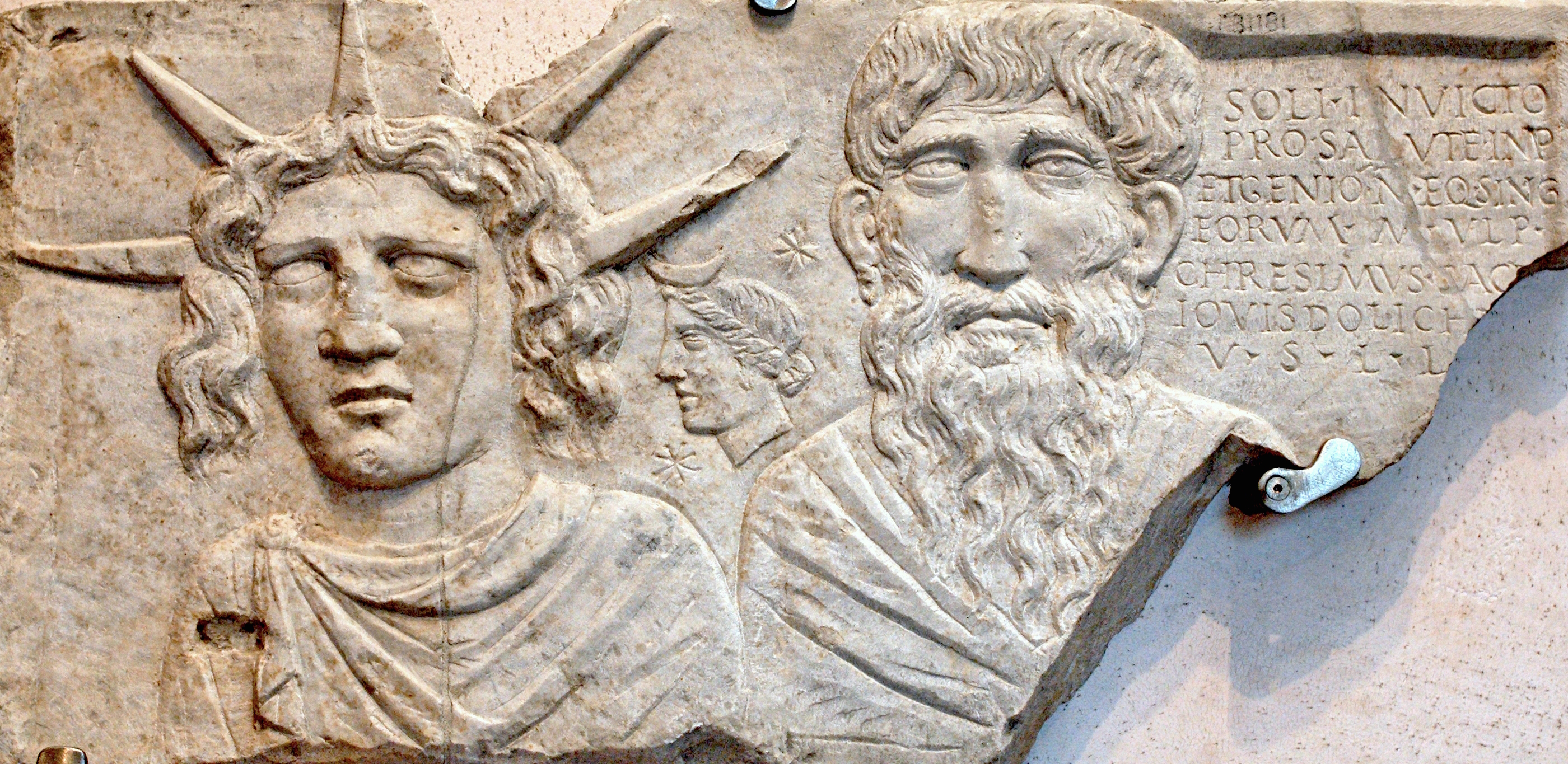
Saturnalia as the ultimate midwinter festival
Saturnalia was an ancient pagan holiday that honored the Roman God Saturn. It took place sometime between December 17th and 24th. It was a week of revelry, decadence and the inversion of social and moral roles.
The festivities consisted of drinking, eating lavishly and giving presents. The first-century poet Gaius Valerius Catullus said that Saturnalia was “the best of times.”
Wealthy Romans paid for the destitute and masters would swap clothes with their slaves. Lucian of Samosata speaking as the god Cronos, boasts about this exuberant time in his poem titled Saturnalia:
During my week the serious is barred: no business allowed. Drinking and being drunk, noise and games of dice, appointing of kings and feasting of slaves, singing naked, clapping… an occasional ducking of corked faces in icy water – such are the functions over which I preside.
Saturnalia began as a rural farmer’s festival to mark the end of the planting season and midwinter.
Both psychologically and cosmically, this is was a unique time of the year for the ancients. The darkness must have affected them tremendously as without the modern advent of artificial lighting, lessened sunlight would have taken a toll on their mental health. During this time sun and stargazers would have also seen the change in the sun’s position.
All of this led to many religious spectacles and spiritual festivals. After all, they were now only relying on their summer food stores of grains and other crops to get them through the winter until they could, again, plant in the new season.
This led to a number of traditions we still take part in today.
Christmas traditions with other pagan origins
Even before historical record, Pagans would worship the trees in the forest and even bring them into their house and start to decorate them. Mistletoe for example was also a plant revered by the Celts and the Norse.
Celtic Druids believed that mistletoe would protect them against the elements of thunder and lightning. These druids would cut off a piece of mistletoe from the trees and then distribute that amongst their people for protection. It was also considered a symbol of peace and joy. Meeting under the mistletoe would call for enemies to put down their weapons and have a truce.
Ivy on the other hand was the great symbol of Bacchus, the Roman equivalent of Dionysus – God of wine, fertility and ritualistic madness. Ivy is a symbol of eternal life.
Traditional Christmas colors like green and red represent fertility. Burning Yule logs was representative of the returning sun as the days began to get longer again.
Christmas revelers, commercial shoppers and devout religious types can all thank the rich traditions and pagan history stretching back thousands of years this holiday season.